Just a few decades ago, a pitched roof was installed exclusively on outbuildings, but thanks to modern materials this became possible in residential construction. Insulation pitched roof is an important component of construction, because this is how you reduce the heat loss of the room and reduce energy consumption for heating it. About how to conduct this procedure This article will tell you as much as possible.
Basic requirements for insulation
The economic side of construction has caused such sharp popularity among private developers. Thanks to a simple roofing structure for relatively little money, you will build decent and durable protection for decades. It is worth understanding that the life of the roof depends entirely on correct calculations and the correct selection of material. Therefore, let's look at the requirements for the thermal insulation layer.
- The insulation should be as airy as possible, since high density will create an increased load on the base of the roof. When selecting and purchasing such material, you must pay attention to its density.
- In addition to its low density, the thermal insulation layer should resist moisture as well as possible. Most materials I know do not meet this requirement, so they have to be wrapped in a waterproofing film or membrane. By the way, if moisture gets into the roofing pie, the water reduces positive traits half insulation. Of course, in the future it will be possible to dry the material, but its former qualities will not return.
- Thermal conductivity is also the main criterion when purchasing thermal insulation. The lower this indicator, the better the product.
- As a rule, residents of private houses try to choose a more environmentally friendly material rather than living next to a source of poison.
- The thermal insulation product must have high fire safety indicators: low degree of flammability and combustion.
- The construction of the material in question must be carried out in accordance with all the rules and regulations of the construction industry. It is especially important that it fits tightly to the base.
- The operational period of thermal insulation largely depends on resistance to changing temperature conditions. In addition, the quality of installation and the type of material itself influence the period.

If you are choosing a good thermal insulation product for a pitched roof, then I advise you to take a closer look at fiberglass, mineral mats or slabs, expanded polystyrene and basalt wool.
As alternative option can be used natural materials, for example, straw, flax, etc., but it is worth understanding that their operational period is much shorter than the previous ones, and the cost may be higher.
How to insulate a pitched roof
Since a pitched roof is very simple in design, creating an additional layer on it will not be difficult. The main part of this roof consists of ordinary beams laid on opposite walls.
It is necessary to think about the insulation of the roofing surface already at the design stage, when the functional purpose of the entire building is decided. If the building is residential, then you will have to purchase quality materials for thermal insulation and lay them during the construction of the roof. Thanks to this, heat from the room to winter time will not go away too quickly, and in the heat the house will be cool.
As is already known, work on the device pitched roof very simple, so to carry out the entire process you will need a small amount of materials, namely:
- Thermal insulation product
- Vapor barrier and waterproofing material
- Stapler or nails
- Carpenter's set
- Construction tape
This list may be supplemented with something else, everything will depend on the coverage you choose.
Sequence of work

As a rule, a pitched roof involves placing beams in increments of 60 centimeters. This value was chosen for a reason, because the standard width of an insulation board or roll has the same distance. Thanks to this step, their installation is as convenient as possible.
- As preparatory work, a vapor barrier layer is attached with inside between the rafter beams. Buttons or staples act as fastening elements.
- To increase the tightness, the joints of the vapor barrier material are glued using construction tape. As for the inside, it should be covered with fiberboard, plasterboard or clapboard.
- Thermal insulation material is laid on the outside. A layer of 15 centimeters is sufficient for good insulation. The product can be divided using an ordinary knife. During the installation process, you need to ensure that the insulation is completely adjacent to the base.
Sharpen it Special attention on the edges of the thermal insulation, they must coincide with the protruding part of the walls. If you need to divide the insulated area into zones, then you can attach a board of suitable size in the right place. At high-quality installation no part of the insulation should extend beyond the rafters.
External insulation installation
In cases where a reinforced concrete slab acts as the roof base, thermal insulation material must be located on the outside. This kind of roofing pie can be found on garages. The structure of the roof is very simple. A vapor barrier is laid on a solid base, then thermal insulation boards, which are covered with waterproofing. Placed on top of the pie concrete screed and installation is already underway on it roofing covering. Now let's look at everything in more detail.
To increase the durability of the roof as a whole, we must not forget about preparatory work. At this stage, the reinforced concrete slabs are cleaned and leveled from dirt and potholes, respectively. The joints between the slabs are also sealed using a special polyurethane foam, withstanding high pressure. As an alternative, fiberglass can be used.
After preparing the base, you can begin laying dense insulation - expanded polystyrene. Laying of such material should be carried out take a running start so that moisture cannot penetrate through the matching seams. As a rule, roll waterproofing is installed on top of the insulation. A cost-effective product is roofing felt. Modern material can last for quite a long period and is very cheap.

A concrete screed is laid on top of the waterproofing. To improve its characteristics, a reinforcing mesh is placed on the waterproofing layer. This way the screed will not crack over time, and the roof of your building will last as long as possible. Absolutely any covering for flat roofs can be mounted on the created layer.
Insulation technology from the inside
Internal thermal insulation includes three layers, namely:
- Waterproofing
- Thermal insulation
- Vapor barrier
This roofing pie is standard for all roofs for residential buildings with a reinforced concrete base or wood sheathing.
In the case when the thickness of the thermal insulation material is less than the rafter leg waterproofing film laid on top of the rafters. If the values are equal, it is attached to bars that extend the load-bearing beams.
The waterproofing is placed across the slope, and the overlap of the strips on each other is at least 10 centimeters. To remove condensation, an air gap of 50 millimeters is arranged between the insulation and the coating. It can be created using small bars prepared in advance. By the way, if you chose mats as thermal insulation, then immediately before laying them do not forget to shake them, this way you will put its structure in order.
If you have to cut the insulation mats, then take 5-10 centimeters more. This will increase the density a little and it will hold up well.
IMPORTANT: Between waterproofing material and the insulation should leave a small gap to ensure natural ventilation. This gap can be created by laying small battens on top of the insulation.
At the next stage of creating a roofing pie, the installation of a vapor barrier layer will be required. It is needed so that incoming moisture from the room below cannot damage the insulation boards. This product is placed underneath the rafters and secured using staple guns or small nails. Vapor barrier, like any other rolled material, should be laid with an overlap of 10 centimeters. To increase the tightness, the joints are taped with construction tape.
On some roofs, the vapor barrier layer is installed in a slightly different way. Its base is the lower part of the insulation, and not the rafter beams. In case of using polypropylene or polyethylene film as a vapor barrier, then waterproofing is installed on top of it. And if breathable membranes were used, then installation is carried out using thermal insulation.

Now we need to say a few words about natural ventilation. High quality ventilation system can be created using 1-2 gaps. One of them should be located between the waterproofing and the roofing. Thanks to this air gap, moisture will naturally leave the roofing pie in the event of condensation or leakage. As for the second, it should be located between the thermal insulation and waterproofing layers. Here the layer will remove condensation and will not allow moisture to accumulate in the insulation.
Suitable materials
In modern construction there are a large number of materials in which you can easily get confused. To make your choice easier, I present to you the three most commonly used insulation materials on pitched roofs.
Mineral wool
The structure of such a material is a system of fibers of an inorganic product that has undergone melting.
It goes on sale in mats or slabs. The following points can be highlighted as positive aspects:
- Low thermal conductivity and sufficient moisture resistance
- Due to its high strength, it can easily withstand all mechanical loads
- Increased sound insulation
- Temperature changes will not affect the structure of the material in any way
- Environmentally friendly product
- Chemical and biological resistance to most substances
- The porosity of the material allows it to retain warm air without any problems
- The original quality of the material is maintained for 15 years
Thermal insulation "URSA"

The advantages of the material are:
- Due to the increased sound insulation, it is more advisable to install Ursa insulation on “loud” roofs, for example, metal tiles
- The elasticity and resilience of the product allows it to be laid on the surface with the greatest possible fit. This allows you to achieve good performance thermal insulation
- This material has good porosity, so it can be divided into parts using ordinary scissors.
- High levels of thermal insulation will help the resident of the house to significantly reduce heating costs
Expanded polystyrene boards
In construction, this product has a second, more well-known name - polystyrene foam. It meets all the requirements of developers and is therefore very popular. The advantages of expanded polystyrene include the fact that it insulates the room very well from extraneous noise, and its structure is not afraid of moisture. Its disadvantages are its low strength, so it is not recommended to place it on soft roofs. In addition, polystyrene foam burns well, which does not correspond to fire safety.
However, if you want to purchase cheap and high-quality material, then I advise you to consider polystyrene foam. It is very light, which means there will be no problems with transportation and delivery of material to the site.
A pitched roof is not so often used for arranging the roofs of private houses, although both the structure itself and its installation are much simpler than a gable roof. It is believed that this type of roof does not retain heat in the house well enough, therefore, it is more often used in the construction of country houses and barns. However, it should be noted that this structure can be made warm and even arranged under it extra room, if the thermal insulation is installed correctly.
A do-it-yourself pitched roof is made according to previously drawn up drawings made on the basis of calculations. This is especially important in cases where it is planned to make living space underneath.
Main advantages and disadvantages of the design
The advantages of this design include the following:
- Saving money on the purchase of building materials.
- Simplicity of design, and therefore of installation.
- Light weight compared to the gable option - less load is placed on the walls.
- High resistance to wind and loads from snow accumulated on the roof.
- The structure can be erected in different angular ranges - from 5 to 45º.
- The pitched roof, made at a slight angle, allows you to install a hot water tank or solar panels on it, as well as create a place to relax.
- Such a structure can be covered with any of the existing roofing materials, of course, taking into account the conditions of its operation and the angle of inclination.

Naturally, like any structure, a pitched roof has its drawbacks, which you also need to know when choosing this option:
- A roof with one slope requires more serious insulation than, since under it there is not such large space, which creates an air gap. Without reliable thermal insulation, the attic space will become very hot in the summer months and cool down in the winter months, in both cases transferring the temperature into the house. However, if you correctly calculate and install all the elements, this drawback can be avoided.
- If the ceiling is made immediately under the roof, arranged at a small angle, then the house loses not only the upper air gap, but also an attic, and therefore the possibility of creating an additional room - this can be considered the second disadvantage of the design. But, if the attic space is planned a little differently, then this drawback can be overcome.

- Another disadvantage of a pitched roof applies only to a structure that has a slight slope of 5-10º - this is poor shedding of snow masses from it. So, if there is a large accumulation of snow, the roof will have to be cleared manually or a heated roof system can be made using a heating cable.

Prices for heating cable and components
Heating cable and accessories
Video: small country house with a pitched roof
Calculation of a pitched roof structure
If you decide to install a pitched roof, then first you need to make calculations and make sure they are correct by seeing with your own eyes the preliminary result in the drawing. Only in this case can you get exactly the option that is ideal for a particular building and its residents.
In order to create such a diagram, you will need to determine the following parameters:
- The total width of the building and the length of the spans between load-bearing walls.
- Estimated slope angle.
- Overall roof length.
- Desired roofing material.
- Height and width of load-bearing walls.
If the roof is planned for country house or, then it is enough to make the front wall of the building slightly higher than the back one to a certain height in order to increase the slope angle.
— The internal distance between the walls will determine how much the rafters should be strengthened and how many beams will be required.
— Before completing the drawing, it is necessary to decide whether it is planned to attic to arrange a living room - the angle of inclination of the slope and the height of the pediment being built will depend on this decision.
— Also, the angle will depend on how much you plan to take out the trump card To to the rooks in front and behind the building.
— In addition, you need to decide on the location of the veranda or terrace, since the roof in front or behind the house may cover it too.
— The above factors directly affect the length, and the total length of the building affects their number.
— The rafters are laid across the building at a distance of 500 to 800 mm from each other. The wider the building, the longer and more massive the rafters should be. Their cross-section varies from 80×150 mm and above. For example, if the rafters are fixed over a span of 6-7 meters, then the cross-sectional size of the rafters must be at least 110x200 mm.
— For the manufacture of rafters, high-quality, well-dried lumber is selected, which does not have cracks and large knots, especially in the areas of their connection with other parts. made from thick boards or timber.
— When the length of the blanks is not enough due to the large width of the structure, they have to be joined. The connection of two parts of the rafters into a single piece is recommended to be placed on support beams or, if they consist of boards, one of them should be located at least 500 mm over the other.

— Sometimes the rafters are even made up of three parts. In this case, the central part of the rafters extends to the outer ones also by a distance of 500 mm.
— To prevent the rafters from sagging over time, they are supported and secured various elements rafter system - struts, crossbars and racks. Such additional details are used if the span width exceeds a distance of 5 meters.
The cross-sectional dimensions of these reinforcing elements must be at least 50×100 mm, and for spacers and beds - 100×150 mm.

— With a span length of 12 m, a stand must be installed in the middle of the floor beam, which also serves to support the rafter leg.
— If the length between opposite walls exceeds 12 m, then, in addition to the rack, additional rafter legs are installed - they will give rigidity to the flooring.
— When the distance between the load-bearing walls is 15 meters or more, there must be at least two racks, and each of the rafter legs is installed as close as possible to the middle of the rafter span between the gable wall and support stand. Additionally, in the center of the structure, the racks are fastened together with a screed bar - this distance should be one third of the width of the building.
- Whatever the angle of the pitched roof, the rafters are laid on the roof, fixed to the walls and to the pediment.

The diagrams show options for supports in rafter systems, with spans of different sizes between the walls. You can easily navigate through them when drawing up a design diagram for a specific building.

The roof drawing must include all necessary information about all sizes of structural elements and the distances between them. Having such a diagram at hand, it will be easy to use it do work, so the drawing must be drawn up very carefully and accurately.
Calculation of the roof slope angle
- It is calculated based on the fact that the roof has the shape of a triangle, in which one angle is always right. This angle is formed by the legs of the floor beams and the pediment part of the structure, and the rafters in this figure play the role of the hypotenuse.

In the presented figure the following are applied symbols:
— Lc- length of the rafter leg;
— Lbc- the height of the pediment from the floor beams to the intersection with the roof plane;
— Lsd– width of the house;
— A– selected or calculated slope angle.
If you remember the basic school course in trigonometry and arm yourself with a calculator, it will not be difficult to calculate all the parameters of the future roof, based on the initial values. The width of the building is easy to measure, and the second parameter can be either the desired gable height or the selected roof slope angle.
So, if the width of the building and the planned height of the pediment are taken as a basis, then the angle of the slope can be easily calculated using the formula:
TgA = Lbc : Lсд
If the calculations are based on the selected angle of the roof slope, then the height of the pediment will be equal to:
Lbc =TgA× Lsd
Lc = Lсд : СosA
At the same time, do not forget that the length of the rafters, calculated in this way, is only up to the intersection with the plane of the walls, without taking into account the canopies on the front and rear sides of the building.
- The slope of the slope angle is selected depending on certain criteria, one of which is the selected type roofing material, since for each of them it is recommended to select a specific value or parameter as close as possible to it, for example:
— Corrugated sheeting requires a slope of at least 8º.
— When using metal tiles, you can make a roof with a slope of 30º.
— For slate, an angle of 20–30° is good.
— For rolled roofing materials, such as roofing felt, as well as other soft roofing, the recommended slope angle is 5-7°, but not less.
If the roof does not have a heating system, and the building is located in a region where there is a large amount of precipitation in winter, then the best option there will be a pitched roof, arranged at an angle of 40-45°, no matter what roofing material it is covered with.
In addition to the above data, you need to understand what types of rafter systems there are.
Types of rafter systems on a pitched roof
When installing a pitched roof, it can be designed in one of three options, the choice of which depends on the type and size of the building:
- A hanging system is installed in rare cases when there are no permanent partitions between the main load-bearing walls. When constructing such a roof, for ease of work, a temporary flooring of boards is laid on the floor beams. On this basis, the trusses of the rafter system are assembled. In order for the hanging system to be reliable, the parallel walls on which the floor beams will be laid must be placed on same height. If necessary, this type of construction is used in houses built from any types of materials used in construction.

If a room is planned in the attic, then ventilation is arranged as for a living space.
If the structure will only serve as an attic, then ventilation must be strengthened, since the room will not be heated. In this case, ventilation must function effectively so that moisture does not accumulate here and dampness and mold do not arise, which will eventually appear in the house.
- Layered rafter systems are distinguished by the fact that they are installed in buildings with internal capital partitions, which become additional supports for floor beams.

In layered systems, the rafters are installed rigidly on the gable wall, on which installed Mauerlat, and their lower edge may be fixed both rigidly and on sliding fastenings. Brick or stone houses are mainly covered with such shed roof structures.
For structural rigidity, additional spacer elements are installed. There are several systems for installing them, depending on how much free space there should be in the attic, the angle of the slope and the massiveness of the rafters.
- The sliding rafter system is used mainly for log cabins, as it avoids deformation of the roof structure if the house shrinks. When installing this type of roof, the rafters are rigidly fixed to the gable wall, on the Mauerlat, and their lower part is attached to the Mauerlat exclusively with sliding fasteners, which, when the walls of the house oscillate, allow the rafters to take a comfortable position.

Installation of a pitched roof
Having specified V all the necessary nuances, having made calculations, drawn up a drawing of the roof and purchased as required for work materials, you can begin to install the structure.
- To make the work easier and safer, the structure must be immediately covered with attic floor beams. They are laid on strips of roofing felt waterproofing laid on the walls. The beams are placed at the same distance from each other as the rafters will be installed in the future - it usually ranges from 500 to 800 mm.

Prices for timber
- On the rear lower wall of the building, along its entire length, a mauerlat made of massive timber is laid on top of the floor beams.
- Next, a flooring of boards should be laid on the beams - it will be safe to walk on it and it will be more convenient to continue the construction of the structure.

- The next stage is the construction of the pediment wall; it is built from the same material as the entire building, or from another, lighter one. For example, if the building is built of brick, then the pediment can be raised from bars and boards.
- Floor beams, previously covered with waterproofing, are embedded in the wall. The pediment is raised to the height specified in the drawing.
- On the gable wall, just like on the opposite wall, the mauerlat beam is fixed.
- Next, markings are made on the lower wall, and fasteners are screwed in to install the rafters.
- On the rafters, for their rigid fastening, according to the drawing, grooves are cut out with which they will be put on on the Mauerlat on the upper wall and the lower one, if provided.

- Then they are secured using special corners and fasteners. On the gable, the rafters are screwed rigidly, while on the lower mauerlat they can be installed in sliding fasteners, depending on the type of structure chosen.

- There is a sequence for cutting in rafters: first, the outermost elements of the entire rafter system are installed, then a cord is pulled along them, which will become a level for the remaining parts. Distance betweenrafters must correspond distance between floor beams.
- For stability, the installed rafters are connected to the floor beams with racks, struts and other elements discussed above. They are secured with metal brackets and corners, which adds rigidity to the structure.
 If it is necessary to extend the rafters beyond the level of the walls, “fillies” are mounted to them
If it is necessary to extend the rafters beyond the level of the walls, “fillies” are mounted to them - If it was intended to extend the roof to construct a terrace or veranda, then external boards called “fillies” are additionally attached to the rafters.
Video: the process of building a pitched roof
Prices for various types of fasteners for rafters
Rafter fasteners
After completing the installation of the rafter system, it is necessary to move on to insulation measures, since a pitched roof especially needs thermal insulation, even if there is a regular attic under the roof.
Suitable for this , descriptions of which can be found on our website by following the link.
The installation of sheathing under the roof or continuous roof sheathing is carried out taking into account the selected roofing material - each of them has its own technology for such work.
Video: continuous sheathing of a pitched garage roof with boards
Installing any roof is a responsible and labor-intensive process, and due to working at height, it is also quite dangerous. Therefore, without having experience in the construction craft, it is better to entrust the installation to craftsmen who know their business, since an unsuccessfully constructed foundation for the roof threatens that the walls of the house will be subject to deformation.
6 main types of rafter systems
| Photo | Name | Rating | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 |
|
⭐ 100 / 100 | ||
| #2 |
|
Hip rafter system | ⭐ 100 / 100 | |
| #3 |
|
⭐ 100 / 100 | ||
| #4 |
|
⭐ 99 / 100 | ||
| #5 |
|
⭐ 99 / 100 | ||
| #6 |
|
⭐ 98 / 100 | ||
Gable rafter systems are the most popular for one-story private houses. They look neat, fit well into any style of construction, are reliable and can be used, depending on the angle of their slope, for arranging an attic under living rooms, utility rooms or simply to create an air gap that retains heat in the building.

- high reliability;
- simplicity of design;
- a gable roof with a slope angle of more than 50 degrees is practically not afraid of snow drifts; a large snow cap will not form on it. Hip rafter system
- for buildings with hip roof pediments are not provided, which greatly reduces the consumption of materials and work for the construction of pediments and filing of overhangs;
- a roof of this type has excellent aerodynamic properties, it is not afraid of strong winds, and the design features will prevent precipitation from entering the attic;
- the surface of such a roof is heated by the sun's rays from several sides at once; on sunny days, the room under an uninsulated roof will be warmer;
- The slopes of such a roof are located at a certain angle, which helps drain rainwater and melting snow from the roof.
- a hip roof is quite complex to design and construct;
- the design of this roof is replete with a large number of connections, beams and rafters, it is necessary to strictly monitor the reliability of all components and connections in order to avoid loss of rigidity and plane shape during the construction of the roof;
- large waste when using most roofing coverings (especially metal tiles).
- additional living space;
- an attic is cheaper than building full second floors or expansion of the perimeter of housing;
- The appearance of a private house with a sloping roof is superior to a classic gable roof.
- the inability to create a spacious room in the attic, because the height of the walls is limited by the roof;
- heat and waterproofing will be carried out over more complex techniques and using special materials;
- Dormer windows increase the requirements for roofing and accumulate more snow.
- reliable, durable and robust design;
- due to the large slope of the roof, the risk of stagnation of melt water and precipitation is reduced to zero;
- fits perfectly with any architectural form;
- the presence of a balanced rafter system.
- complexity of installation work;
- arrangement of a large number of valleys;
- high consumption of building and roofing materials;
- complex care and maintenance of the structure.
- not subject to deformation;
- the snow does not linger;
- it will perfectly withstand strong winds, for regions where hurricanes and tornadoes are not uncommon - a big plus;
- eaves overhangs are less susceptible to damage.
- differs in higher cost than gable;
- the design turns out to be complex, usually the construction of a hip roof is entrusted to specialists, and this is again an additional expense;
- equipping an attic under a hip roof is a difficult task, often simply impossible.
- efficiency (almost double savings in lumber and roofing materials compared to a gable roof);
- insignificant weight of the roof (makes it possible to erect it on buildings with a lightweight foundation without the use of lifting equipment);
- the possibility of installing a pitched roof on large houses;
- maintainability (ease of movement on the roof, especially at small angles of inclination);
- high dependence on snow loads (requires correct calculations of sections of structural elements during design);
- enhanced thermal and waterproofing of the roof (important at small angles of inclination);
- unsightly appearance, which requires increased attention to the quality of facade work and the use of modern roofing materials.
Attic rafter systems are called broken, which are used in cases where it is planned to attic space arrange a living space, since this design creates the most spacious area for future rooms. Each of the two slopes of the broken rafter system consists of two planes - the top and the side.

The multi-slope rafter system can be called the most complex of all existing ones, since it often includes different roof shapes - it can be gable and single-pitch, hipped, hip or half-hipped in various combinations. This option is chosen for houses with complex internal layouts, and there are more and more of them in recent years.

Hip roofs have four slopes, with the gable sides having a shallow triangular shape, and the side slopes of the structure being trapezoidal. It is the triangular slope that is called the hip - it joins the trapezoidal plane at a certain angle.

As can be understood from the name, this roof has one slope, located at a slope. If the building is small in size and is entirely built from brick or concrete, then the rafters of the structure are laid on the high load-bearing façade wall and on the low rear wall. If the distance between the façade of the building and the rear wall is six meters or more, then retaining posts are installed between the front and rear walls.
A house built and furnished with one’s own hands is the real pride of any owner. An integral stage in the arrangement of any residential building is internal insulation roofs. And if in most cases no problems arise with the thermal insulation of walls, then the insulation of the roof structure can confuse an untrained craftsman. Therefore, before starting the practical part, study all the theoretical recommendations proposed below.

After installing the insulation and all related elements, the roofing system will look like a layer cake. The design is based on a rafter system. All other elements are laid and secured onto it.

Modern roofing “pie”
In the classic version, the layers of the pie, starting from the finishing roofing, are placed as follows:
- roofing;
- lathing for installation of finishing material. Can be solid or sparse;
- counter-lattice bars. Needed to create a ventilation gap under the roofing material;
- waterproofing film;
- thermal insulation material;
- vapor barrier material;
- lathing for installation of insulating materials and internal cladding;
- inner lining material.
A properly installed roofing pie will significantly reduce heat loss in cold weather and prevent overheating of the space under the roof in hot weather. Waterproofing will protect the insulation from atmospheric moisture, and the vapor barrier material will prevent the formation of condensation and the occurrence of all related problems.

How to insulate?
The modern market offers a huge range of materials that can be successfully used for internal roof insulation. Try to avoid excessive savings - materials must be of high quality.
Insulation parameters

When choosing suitable insulation you need to pay attention to a number of basic characteristics of the material, namely:
- weight. The heavier the insulation, the more significant load it will place on the roof. This imposes a number of additional requirements on the rafters and sheathing - their configuration and strength must correspond to the characteristics of thermal insulation;
- thermal conductivity. It is better for this parameter to be as low as possible, if possible no more than 0.04 W/m*C;
- resistance to adverse external influences.
Preferred insulation materials

Not many materials meet the above requirements. Among all the existing insulation options, professionals recommend giving preference to mineral wool insulators and foam panels. Other than that equal conditions mineral wool is more preferable.
Additional insulating materials
In combination with insulation, the roof will need to be additionally insulated using vapor and moisture insulation materials. For roof waterproofing, polyethylene and roofing felt are usually used. These materials are highly resistant to moisture.

The vapor barrier layer is best equipped using special membranes, glassine or modern foil materials.
Regardless of the chosen insulation (installation is still carried out in the same sequence), during the work process you must adhere to a number of basic recommendations, without which you cannot count on high-quality internal insulation of the roof.

All the rules can be combined into one brief summary of tips, namely:

Thus, even before starting thermal insulation work, the master needs to study a fairly large amount of information and remember a number of important requirements. The work must be done to the highest possible quality. Properly equipped insulation will make living in the house as comfortable as possible and will significantly reduce the cost of heating the premises.

Use the recommendations received and remember: insulation must be done with the obligatory installation of vapor barrier and moisture barrier layers. Only such a complex will make it possible to obtain a reliable, durable roofing system that is resistant to any adverse external influences. It’s better to immediately do everything according to the rules and live peacefully in safe home than patching holes in roofing pie after every heavy rain.

Preparing for roof insulation
The insulation procedure remains almost the same regardless of the type of roof, materials used and other points. Having understood the main points of thermal insulation work, you will be able to successfully apply them in practice.
First of all, carefully prepare the roof for the upcoming internal insulation.
First step. Inspect the rafter system. If you find rotted or damaged elements, replace them with new parts.
Second step. Process everything wooden elements antiseptic.
Third step. Check the condition of pipelines and electrical wiring if these communications are laid under the roof.
Guide to internal roof insulation

Start working on the internal insulation of the roof. The event is held in several stages. Go through each of them sequentially, not forgetting the recommendations received earlier.
It is assumed that the rafters, sheathing and other necessary elements have already been installed and all you have to do is install the insulating materials and then lay the final roofing covering.
The first step is vapor barrier

Lay the film with a 10-centimeter overlap. To attach the vapor barrier to the bars, it is convenient to use a construction stapler with staples. Double-seal all joints with duct tape. Be especially careful and thorough when sealing various difficult areas, such as the junction of the film with pipes, walls and other structural elements.
The second step is insulation

EKOTEPLIN - roof insulation
Place the selected insulation in the cells of the sheathing. Usually the sheathing is assembled so that the step between its bars is a couple of centimeters less than the width of the insulation, so you can place the insulating boards as tightly as possible. The sheathing bars themselves must be nailed to the rafters perpendicular to them.

If you really want, you can do without lathing - you hammer nails along the edges of the rafter legs and stretch the wire between them. It will hold the insulation boards. However, it is better not to give up the sheathing - it is safer with it.
The insulation itself is usually laid in 2 layers. In this case, the top layer must be laid with a certain offset in relation to the bottom one - it is impossible for the joints of the insulation boards of both layers to coincide.

Third step - waterproofing
Place the waterproofing film so that it completely covers the insulation, sheathing and rafters. To fix the film, it is most convenient to use a construction stapler with staples.

Place waterproofing under the roof overhang - this will create the conditions necessary for effective water drainage in the future.
At the end, all you have to do is lay the selected roofing material on the roof.
Thus, although independent internal insulation of the roof is a very important and responsible undertaking, there is nothing overly complicated in its implementation. Do everything according to the instructions, and very soon your home will become truly cozy and warm, and heating costs will be reduced. cold season years will decrease significantly.
Good luck!
Video - Do-it-yourself roof insulation from the inside
If you want to build an extraordinary house, unlike your neighbors’ house, take a closer look at houses with a pitched roof. It gives the building originality. In addition, a pitched roof is the simplest to install. So simple that you can easily do it yourself.
Advantages and disadvantages
Shed roofs are considered the most inexpensive and easiest to install. And this is true, especially with the small width of the building. However, in our country, houses with pitched roofs are very rare. For the most part, this is due to the fact that two or four pitched roofs are more familiar to us - they look more familiar. The second snag is to find a project adapted to our weather conditions. There are a lot of projects on Western resources, but they are designed for a milder climate and, as a rule, have a large glazing area. Finding an architect who will competently change a project you like is very difficult. But if you succeed, and the harmony of the building is not disturbed, the house turns out to be very original.
Many people are afraid of uneven ceilings in some parts of the building. They are, of course, more difficult to beat than standard ones, but the result is of a completely different level - 100% original. True, this time it is very difficult to find a designer who can develop such an interior in the vastness of our Motherland, but nevertheless, it is possible.
There is another way out - to level the ceilings by overlapping, and use the free space under the roof as technical rooms. Such options have been implemented and the owners are very satisfied. Yes, technical rooms are in ground floor, and at the top, but there are no problems with groundwater.
These are, perhaps, all the disadvantages or pitfalls that a pitched roof can bring. There is, however, one more point that can hardly be called a disadvantage. Due to the peculiarity of the structure, the roofing material on such houses is not visible from the ground. If the terrain is flat, without large differences in elevation, there is no point in bothering with the appearance of the roof. It is better to choose simple-looking, but high-quality materials, quiet (the flat surface is large, it makes a lot of noise when it rains) and reliable. One of the popular options is seam roofing. It provides the proper degree of tightness and is not very noisy. Another option is made from modern materials. Such roofs are even quieter, and modern materials can be used for 20-30 years without repair.
Construction of a pitched roof
Organize the required slope of the pitched roof due to the difference in heights of the opposite walls. One wall of the building turns out to be significantly higher than the other. This leads to increased consumption of materials for the walls, but the rafter system is very simple, especially for buildings of small width.

With sufficient bearing capacity walls, the truss system of a pitched roof rests on a mauerlat attached to the wall. To make the load distribution more uniform, the top row of the wall masonry is reinforced with longitudinal reinforcement (for brick walls, from concrete blocks) or an armored belt is poured over the last row (for walls made of limestone, shell rock). In the case of a wooden or frame structure, the role of the Mauerlat is usually performed by the last crown or top trim.
If the building material of the walls is insufficiently strong, most of the load can be transferred to the ceiling. To do this, install racks (steps of about 1 meter), on which purlins are laid - long bars running along the building. The rafter legs then rest on them.

When pouring an armored belt or laying the last row, studs are installed into it in increments of 80-100 cm, with the help of which the mauerlat is then attached to the walls of the building. In wooden houses, if you do not make an armored belt, it is impossible to install studs. In this case, installation on pins with a hexagonal head is allowed. Under the pin, through the Mauerlat, a hole is drilled, a couple of millimeters smaller than the diameter of the pin. A metal rod is hammered into it, which attracts wooden beam to Wall. The connection is tightened using a hex wrench of the required size.
Rafter system of a pitched roof
Such roofs are especially popular in the construction of courtyard buildings - sheds, garages. It’s just that the size of the buildings allows the use of not very powerful beams, and beams are required in small quantities. With a building width of up to 6 meters, the rafter system of a pitched roof contains almost no additional reinforcing elements (supports and purlins), which is beneficial. Also attractive is the absence of complex knots.
For Middle zone In Russia, for a span of up to 5.5 meters, beams of 50-150 mm are taken; up to 4 meters, 50-100 mm is enough, although in an amicable way, you need to consider the snow and wind load specifically in your region, and, based on this, determine the parameters of the beams .

With a distance between the walls of up to 4.5 meters, the pitched roof consists of two mauerlat bars fixed to the walls, and rafter legs that rest on the mauerlat. Really very simple design.
With a span width of 4.5 meters to 6 meters, a support is also required, fixed to a higher wall at the floor level and a rafter leg that rests on the beam almost in the middle. The slope angle of this beam depends on the distance between the walls and the level of installation of the beam.
More complex rafter systems in a pitched roof with a building width of more than 6 meters. In this case, it is optimal if the house is designed in such a way that there is also water inside bearing wall, on which the racks rest. With a house width of up to 12 meters, the trusses are still simple, and the cost of installing the roof is minimal.

For buildings more than 12 meters wide, the system becomes more complex - there are more rafter legs. In addition, manufacturing beams longer than 6 meters is expensive. If an increase is required only by the width of the roof overhangs, the beams are extended along the edges with fillets. These are pieces of beams of the same cross-section, connected to the beam and secured on the sides with two wooden plates at least 60 cm long, fastened with bolts or nails, allowing the use of mounting plates.

If the total length of the beam is more than 8 meters, they are usually spliced. The joints are further reinforced by nailing boards or mounting plates.

Options for attaching the rafters to the mauerlat: sliding at the top and rigid at the top on the right. Below on the right is a version of a tie-in without overhangs (very rarely used)
There may also be questions about how to attach the rafters of pitched roofs to the Mauerlat. Fundamental differences No. Everything is also in rafter leg They make a cutout with which the beam rests on the mauerlat. In order not to suffer with each rafter leg, leveling its fit, having cut out the first one, a template is made from a piece of board, thick plywood or timber that exactly repeats the resulting “cut”. All subsequent rafters are sawn before installation. A template is applied to them in the right place, a recess of the required shape and size is outlined and cut out.
This was about rigidly attaching the rafter legs to the mauerlat. It is used on all buildings that exhibit low shrinkage. This method of fastening cannot be used on wooden houses - the house always settles or rises slightly, which can cause misalignment. If the roof is fixed tightly, it may tear. Therefore, when installing a pitched or any other roof on wooden houses, a sliding connection of rafters and mauerlat is used. For this there are so-called “slippers”. These are plates, consisting of corners that are attached to the mauerlat and metal strips movably connected to them, which are attached to the rafter leg. Two such slips are placed on each rafter.
Choosing a roof angle
The roof slope angle is determined by a combination of indicators - wind and snow loads and the type of roofing material. First, the angle is determined according to climatic conditions (depending on the amount of precipitation and wind loads). Then they look at the minimum recommended slope for the selected type of roofing material (in the table below).
If the desired angle is greater, everything is fine; if it is less (which happens very rarely), increase it to the recommended one. It is not advisable to make a roof with an angle less than the minimum angle recommended by the roofing manufacturer - it will leak at the joints. To make it easier to navigate, let’s say that for central Russia the recommended slope of a pitched roof is 20°. But it is advisable to calculate the figure for each region, and even for different locations of buildings on the site.
By the way, keep in mind that different manufacturers of the same type of roofing material may require different minimum slope. For example, one brand can be produced on roofs with a minimum slope of 14°, another - 16°. And this despite the fact that GOST defines a minimum slope of 6°.
It is also worth remembering that with a slope of up to 12°, in order to ensure the tightness of any roofing material, it is necessary to coat all joints of the material with a liquid waterproofing compound (usually bitumen mastic, less often - roofing sealant).
Determine the height to which you want to raise the wall
To ensure the found slope angle of the pitched roof, it is necessary to raise one of the walls higher. How much higher we will find out by remembering the formulas for calculating a right triangle. Using them we also find the length of the rafter legs.

When calculating, do not forget that the length is obtained without taking into account overhangs, and they are needed to protect the walls of the house from precipitation. The minimum overhang is 20 cm. But with such a small protrusion beyond the building, the pitched roof looks short. Therefore, overhangs of at least 60 cm are usually made on one-story buildings. On two-story ones they can be up to 120 cm. In this case, the width of the overhang is determined based on aesthetic considerations - the roof should look harmonious.

The easiest way to determine how much the roof needs to be extended is in design programs that allow you to draw the building to scale and “play” with the overhangs. Everything should be displayed in 3 dimensions (most popular program ScratchUp). Twist through different sizes of overhangs, decide which one looks better (if there is no project), and then order/make rafters.
Photo report from the construction site: a pitched roof on a house made of aerated concrete
A house was built in St. Petersburg. There was no project, there was a general idea, which is presented in the photo. House made of aerated concrete, finishing- plaster, seam roof chosen on the basis of low cost, reliability, and ease of installation.

After the walls were removed, an armored belt was poured into them, into which studs (Ø 10 mm) were installed every meter. When the concrete in the armored belt reached the required deterioration, a layer of waterproofing (“Gidroizol”, cut lengthwise into strips of the required width) was laid on the bitumen mastic. A mauerlat - 150-150 mm timber - is laid on top of the waterproofing. All lumber used for roofing is dry and treated with protective impregnations and fire retardants.

Beginning of installation of a pitched roof - laying the Mauerlat
First, they put it in place (lying on the pins, held by assistants), and walk along it, hitting with a hammer on the places where the pins are. The places where the studs stick out are imprinted in the timber. Now they drill holes and simply push it onto the studs.
Since the span turns out to be large, supports made of timber (150-150 mm) were placed on which the purlin was laid, which will support the rafter legs.

The width of the roof is 12 meters. This takes into account a 1.2 meter offset from the front side. Therefore, the Mauerlat bars and the purlin “stick out” beyond the walls exactly at this distance.

At first there were doubts about such a large offset - the rightmost beam hangs 2.2 meters. If this offset is reduced, it will be bad for the walls, and the appearance will deteriorate. Therefore, it was decided to leave everything as it is.

Laying rafters
Rafters are laid from two spliced boards 200*50 mm, with a pitch of 580 mm. The boards are nailed together in a checkerboard pattern (top-bottom), with a pitch of 200-250 mm. Nail heads are sometimes on the right, sometimes on the left, in pairs: Two on top/bottom on the right, two on top/bottom on the left, etc.). We space the joints of the boards by less than 60 cm. The resulting beam is much more reliable than a similar solid beam.


Next, the pie of a pitched roof for this case is as follows (from the attic to the street): vapor barrier, stone wool 200 mm, ventilation gap (sheathing, counter-sheathing), moisture insulation, roofing material. In this case it is dark gray pural.

We will carry out insulation from the inside later, but for now we are laying a Tyvek Solid hydro-windproof membrane (vapor-permeable) on top of the rafters.

The membrane is laid from bottom to top and secured with staples. The fabric that is rolled out higher overlaps the one already laid by 15-20 cm. The joint is sealed with double-sided tape (bought together with the membrane). Then the planks are placed on top of the membrane, and on them is a sheathing for a standing seam roof.

First, the sheathing was made from 25*150 mm boards in increments of 150 mm. After installation, walking around the roof, it was decided to strengthen the sheathing. To do this, we fill 100 mm wide boards between the already laid boards. Now there is a gap of 25 mm between the boards.

Sheathing a pitched roof as a result
Next, hooks were placed on the lower gable. They are filled unevenly, since due to the large length of the pediment, it was decided to make two receiving funnels at a distance of 2.8 meters from the edge. To ensure drainage in two directions, such a relief was made.

Next, you need to bring in pieces of metal (pictures) 12 meters long. They are not heavy, but they cannot be bent, so the “sled” disappears. For lifting, a temporary “bridge” was built connecting the ground and the roof. The sheets were lifted along it.

Next come roofing, which differ depending on the type of roofing material. In this case, it was necessary to solve the problem of thermal expansion of the material - galvanized steel (pural) significantly changes its dimensions when heated/cooled. To ensure freedom of expansion, it was decided to fasten the material to the sheathing by the seam using movable clamps with a freedom of movement of 15-20 mm.


After laying the roofing material, what remains is the lining of the overhangs, and they are no different.

The roof needs to be brought to perfection - the overhangs need to be hemmed, but basically it is already ready
Well, the photo below shows what happened after finishing. Very modern, stylish and unusual.

House with a pitched roof - finishing is almost finished
Projects and photos of houses with a pitched roof
As has already been said, it is difficult to find interesting designs of residential buildings with a pitched roof. So far, these buildings are unpopular with us. Perhaps just because of its originality. This section contains several projects or photos of already built houses. Maybe it will be useful to someone, at least as an idea.






Large windows are beautiful, but irrational in our climate

Multi-level house - an interesting completed project

This is a prototype of what is located above

Original house. Under one pitched roof there is a house and outbuildings, and part of it is a canopy over the yard between two buildings


Insulation of the roof of a private house or cottage - necessary condition for living in it during the winter in Russian climatic conditions. According to a well-known physical law, heat always rises, which means that its main losses should be sought precisely in the roof structure. Without proper thermal insulation of the roof, any attempts to warm the room well will not be successful.
Roof insulation is a necessary energy-saving element, and all costs for its installation will pay off quickly. Modern technologies and traditional traditional methods allow you to solve the question of how to properly insulate the roof of a house yourself.
Features of roof insulation
The main goal of any insulation is to create reliable thermal insulation between the room and the outdoor environment. Thermal insulation of the roof must take into account the presence of a significant temperature difference on the internal and external surfaces, the likelihood of exposure to sedimentary moisture from above and exposure to steam from below. The design must provide waterproofing, vapor tightness and prevent the accumulation of condensate.

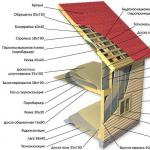
Figure 1. Roof insulation diagram.
The thermal insulation system of the roof is determined by the design of the roof itself. Insulation of a pitched roof or a gable rafter roof can be carried out, as well as flat roof, when it is possible to lay insulation, both outside and inside. Various options thermal protection requires an attic. It can act as a habitable attic, and then it is necessary to insulate both the roof slope and the ceiling. The attic may be cold, in which case only the ceiling is insulated.
The material of the structure also creates its own specificity. Naturally, it is possible to insulate the roof of a wooden house with wooden floor beams only with lightweight thermal insulation, and if there is concrete floor the possibility arises of using bulk heavier materials. The design of the thermal roof barrier also depends on the purpose of the structure - residential building, bathhouse, outbuilding, etc.
Return to contents
Types of thermal insulation structures
Thermal insulation of the roof can be made from materials different types forms ready for use. Currently, a wide range of different building materials is offered, and it is important to choose the right option.

Figure 2. Scheme of roof insulation from the inside.
The main ready-made forms include the following types of insulation:
- Roll materials. Such thermal insulation materials are produced on the basis of mineral and glass fiber (including mineral wool), single-layer or multi-layer polymers. The standard thickness of the material is 5, 7.5, 10, 15 and 20 cm, the width of the roll is 35-50 cm. The length of the fabric on the roll can reach 8-10 m.
- Non-rigid sheet material. Polymer sheets and plates of different thicknesses are widely used. The most common material is polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam.
- Plates. To the tough durable materials with thermal insulation properties include: mineral pressed boards, chipboard, fiberboard. Wood sheets are usually used in conjunction with rolled materials.
- Bulk thermal insulation. If there are horizontal surfaces of sufficient strength, thermal insulation is often made from bulk material With different sizes factions. The most typical representatives: expanded clay, ash, basalt, sawdust.
- Aluminized elements. A modern heat insulator is often combined with a vapor barrier, which is provided by a layer of aluminum foil. Such materials are available in the form roll material. In addition, aluminized thermal insulation mats are available.
- Blown material. Modern materials include polymer thermal insulation materials, which are blown with foam in a layer of 250-300 mm. Insulation with such foam allows for high thermal insulation properties after the substance has hardened.
Return to contents
Selecting material for insulation

The correct choice of thermal insulation material will ensure optimal insulation roofs at minimum sizes and mass. The most used materials include: fiberglass (wool), mineral wool, basalt, polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam, expanded clay.
Mineral wool is one of the most common insulation materials. It has excellent thermal insulation properties. Available in the form of rolls and slabs with a thickness of 5 to 20 cm. The main disadvantage is hygroscopicity, which requires careful protection from water penetration. The most famous domestic manufacturers: Thermosteps, AKSI, Izorok, Mineral Wool, as well as the companies Ragos (Finland), Rockwool (Denmark), Izomat (Slovakia).
Glass wool has increased durability and strength. Available in the form of slabs and mats. The most famous materials are those produced by Flyder-Chudovo, URSA, and Izover.
Expanded clay is a bulk thermal insulation material with very low thermal conductivity, good sound insulation, and non-flammability. Absolutely safe for the environment. The substance has very high frost resistance and resistance to temperature changes.

Figure 3. Scheme of external thermal insulation of a flat roof.
Expanded polystyrene or polystyrene foam is widely popular due to its high thermal insulation characteristics and low specific gravity. Requires additional waterproofing.
Extruded polystyrene foam of the M35 and M50 brands from TIGI-Knauf does not have this drawback.
There are good reviews when insulating roofs using semi-rigid sheets such as Penoplex and Styrofoam.
Sprayed polyurethane foam and polyisocyanurate foam insulation is one of the most modern thermal insulators. They have high water resistance.
While it exists main drawback — high price and necessity special equipment for overlay.
Return to contents
Production of roof insulation

When installing roof insulation with your own hands, you will need the following tools:
- Bulgarian;
- electric drill;
- perforator;
- screwdriver;
- hacksaw;
- plane;
- hammer;
- chisel;
- scissors;
- furniture stapler;
- shovel;
- paint brush;
- construction level;
- roulette.
Insulation of the roof of a house is carried out taking into account the roof structure, the presence of an attic and its purpose.
Return to contents
Roof with slope

If non-residential cold attic or thermal insulation of a pitched roof, then the thermal insulation is laid between the ceiling beams. When using mineral wool the sequence of operations is as follows: running joists are applied to make it possible to walk on the ceiling without deforming the wool, then a membrane is laid to allow steam to pass through and ventilate the wool, insulation is laid, and everything is covered with OSB boards on top. The roof insulation scheme is illustrated in Fig. 1.
For a cold attic it is worth considering a wonderful and more cheap option- roof insulation with sawdust. If ceiling has high strength, it can be used bulk heat insulator(for example, expanded clay).
Roof insulation when planning a habitable attic requires more complex process. In addition to constructing a heated floor using the described technology, it is necessary to insulate the roof slope. In this case, the thermal insulation material is fixed between rafter system. A diagram of such thermal insulation is shown in Fig. 2.

Installation of pitched insulation is carried out in the following order:
- A layer of waterproofing is applied over the roofing sheathing, and it is secured with counter battens.
- Expanded polystyrene slabs (or other insulation) are laid between the rafters so that there are no gaps (it is advisable to use a two-layer application of insulation, and the gaps between the slabs should be covered with a solid slab).
- Applying a vapor barrier in the form of a polymer film with a layer of foil or a special vapor-permeable membrane, and fastening to the rafters using a furniture stapler. The sheets are superimposed with an overlap of at least 10 cm and connected with tape.
- Installation of decorative ceiling covering.