Nowadays, batteries are the most common power sources for electronics and small appliances. The need to replace them arises quite often. In order to make the best choice when purchasing a new voltaic cell, you should pay attention not only to the size of the batteries and the name of the manufacturer. This article will answer the following questions: What form do these power supplies come in? What are the sizes? How are galvanic cells marked and what should you pay attention to when purchasing so that the power source lasts a long time?
Types of batteries
Batteries are classified depending on the materials from which their active components are made: anode, cathode and electrolyte.
There are five types of modern power supplies:
- saline,
- alkaline,
- mercury,
- silver,
- lithium
Battery types by size will be listed below. Now let’s take a closer look at each of these classes of galvanic cells.
Salt batteries
Salt batteries were created in the second half of the twentieth century. They replaced the previously existing manganese-zinc power sources. The dimensions of the batteries have not changed, but the manufacturing technology of these galvanic cells has changed. Salt power supplies use ammonium chloride solution as the electrolyte. It contains electrodes made of zinc and manganese oxide. The connection between the individual electrolytes is carried out using a salt bridge.
The main advantage of such batteries is their low cost. These galvanic batteries are the cheapest among all existing ones.
Disadvantages of salt batteries:
- during the discharge period the voltage decreases significantly;
- the shelf life is short and is only 2 years;
- by the end of the guaranteed shelf life, the capacity is reduced by 30-40 percent;
- at low temperatures the capacity decreases to almost zero.
Alkaline batteries
Such batteries were invented in 1964. Another name for these power sources is alkaline (from the English word alkaline, which means “alkaline”).
The electrodes of such a battery are made of zinc and manganese dioxide. The electrolyte is potassium hydroxide alkali.
Today, these batteries are the most common, because they are perfect for most electronic devices.
Advantages of alkaline power supplies:
- have a larger capacity compared to salt ones and, as a result, a longer service life;
- can operate at low ambient temperatures;
- have improved tightness, that is, the likelihood of leakage is reduced;
- have a longer shelf life of 5 years;
- have a reduced self-discharge rate compared to salt batteries.

Disadvantages of alkaline power sources:
- the discharge period is characterized by a gradual decrease in the output voltage;
- The dimensions of alkaline batteries are similar to those of salt batteries, but the cost and weight of alkaline power sources are higher.
Mercury batteries
In such a battery, the anode is made of zinc, the cathode is made of mercury oxide. The electrodes are separated using a separator and a diaphragm, which is saturated with a 40% potassium hydroxide solution. Alkali is used here as an electrolyte. Thanks to this composition, this power source can work as a battery. But during cyclic operation, the galvanic cell degrades and its capacity decreases.
Advantages of mercury batteries:
- stable voltage;
- high capacity and energy density;
- ability to work at both high and low ambient temperatures;
- long shelf life of 10 years.
Disadvantages of mercury power sources:
- high price;
- the possibility of hazardous exposure to mercury vapor in the event of depressurization;
- the need to establish a collection and recycling process.
Silver batteries
A silver battery uses zinc for the anode and silver oxide for the cathode. The electrolyte is sodium or potassium hydroxide.

- voltage stability;
- the presence of high capacity and energy density;
- immunity to ambient temperature;
- long service life and storage.
The disadvantage of such batteries is their high cost.
Lithium batteries
In such a battery, the cathode is made of lithium. It is separated from the anode using a separator and a diaphragm, which is impregnated with an organic electrolyte.
Advantages of lithium batteries:
- constant pressure;
- high capacity and energy density;
- independence of energy intensity from load current;
- small weight;
- long shelf life, up to 12 years;
- immunity to temperature changes.

The only disadvantage of lithium batteries is their high cost.
As stated above, power sources have different chemical compositions. The shapes and sizes of batteries also differ significantly from each other. Galvanic cells have different heights, diameters and voltages. Let's consider the classification of batteries in accordance with these parameters.
Depending on the voltage, height, diameter and shape, power supplies can be systematized in a certain way. One of the most popular classification systems is the American one. It is shown in the figure below. This standardization is convenient and is used in many countries.

According to the American system, power supplies are classified as follows:
Name | Height, mm | Diameter, mm | Voltage, V |
In addition to the class indicated in the table, power supplies also have a common name that is used among the people. For example, the size is comparable to the size of a human finger, so the “popular” name for this galvanic cell is a “finger-type” battery, or “two A”. But the power source C is commonly referred to as a “thumbelina”. Galvanic cell D is called a “barrel”. And the dimensions of which are similar to the parameters of the smallest human finger, it is not for nothing that it is called “little finger”, or “three A”. The source was called “crown”.
Also in electronics, miniature round batteries are widely used, the sizes and names of which are varied. More detailed information about silver “pills” and the classification of such power sources is given below.
Tablet batteries: sizes and names
Another name for a miniature round battery is a dry cell. Such power supplies consist of an anode made of silver oxide, a zinc cathode and an electrolyte. The latter is a mixture of salts, which has a paste-like consistency.
Different manufacturers often assign designations to such power supplies that differ from the standard ones. Below is a classification table showing alternative names and sizes of watch batteries.
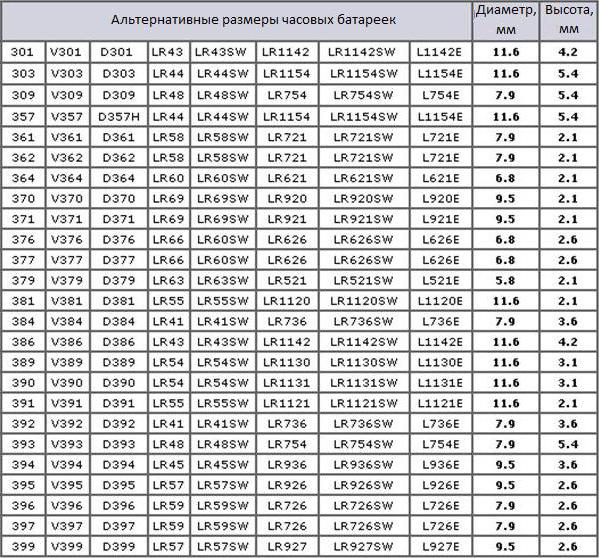
It is these miniature silver “tablets” that make the mechanisms of modern wristwatches work. When it comes time to replace the battery, you may be faced with the question of what power source is suitable in this situation? For example, if the watch used a 399 cell, you can replace it with a miniature battery, which, depending on the manufacturer, may be called V399, D399, LR57, LR57SW, LR927, LR927SW or L927E. Under these names a “tablet” will be produced, the height of which is 2.6 millimeters and the diameter is 9.5.
Battery size is not the only parameter you should pay attention to when purchasing power supplies. In order to learn how to decipher the information that is located on galvanic cells, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic principles of their marking.
Battery markings
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has created a specific designation system according to which all batteries should be labeled. The power supply housing must contain information about its energy capacity, composition, size, class and voltage. Using the example of the battery shown below, let’s take a closer look at all the marking elements.

The information on the power supply indicates the following:
- the electric charge of the galvanic cell is 15 A*h;
- power source class - AA, that is, it is a finger-type battery;
- the voltage is 1.5 Volts.
What does the inscription "LR6" mean? This, in fact, is the marking, which provides information about the chemical composition and class of the power source. The types of batteries have the following letter designations:
- saline - R;
- alkaline - LR;
- silver - SR;
- lithium - CR.
Battery classes are indicated by the following numbers:
- D - 20;
- C - 14;
- AA - 6;
- AAA - 03;
- PP3 - 6/22.
Now you can decipher the LR6 marking in the above figure. The letters here indicate that this is an alkaline galvanic cell, and the number indicates the size of the AA battery, that is, it indicates that the power source belongs to class AA.
Scope of application and features of battery selection
First of all, it should be noted that all galvanic cells meet the requirements of unification, that is, the consumer can easily replace a power source from one manufacturer with a similar battery from another. There is only one caveat: you should not use current sources manufactured by different companies or, especially, of different types in one device. This will significantly reduce the battery life.
When choosing power supplies, you need to pay attention to the packaging. Often the manufacturer indicates on it the devices in which it is recommended to use these batteries. If such information is not provided, the tips below will help you make the right choice.
Salt batteries have a low capacity of 0.6-0.8 Ah and are used in devices with low power consumption. These can be remote controls, electronic thermometers, testers, floor or kitchen scales. Salt elements can also be used as The dimensions of such current sources are similar to the corresponding parameters of alkaline ones, however, their areas of application differ significantly. After all, if you use salt batteries in devices with an electric motor, flashlights or cameras, their service life can be only 20-30 minutes. Such galvanic cells are not designed for heavy loads.
Alkaline batteries have a fairly large capacity of 1.5-3.2 Ah. This allows them to be successfully used in devices that have high power consumption. Such devices include digital cameras with flash, flashlights, children's toys, office phones, computer mice, etc. Batteries designed specifically for cameras release energy faster. This has a positive effect on the speed of the cameras. If you use an alkaline power source in devices with low power consumption, the batteries will show excellent results, their service life will be several years.

Twenty to thirty years ago, mercury batteries were widely used in devices such as pacemakers, hearing aids, and military devices. To date, the use of these power sources is limited. In many countries, the production and use of such voltaic cells is prohibited due to the fact that mercury is a toxic substance. If these power sources are used, it is necessary to organize their separate collection and disposal in accordance with safety requirements.
Silver batteries have not become widespread due to the high cost of the metal. However, miniature power supplies of this type are widely used in wristwatches, laptop and computer motherboards, hearing aids, musical cards, key fobs and other devices where it is impossible to use larger batteries.
Lithium batteries have a longer lifespan than even the best alkaline ones. Therefore, such power supplies are used in devices that have high power consumption. This could be computer and photographic equipment, medical equipment.
Conclusion
A battery is a product that, despite its small size, can be dangerous. You cannot disassemble the power source, throw it into a fire, and, of course, try to recharge it. You can find tips online on how to give your battery a second life. Do not attempt such experiments as it may be dangerous.
When purchasing new batteries, you should pay attention not only to the manufacturer and suitable sizes, but also to the chemical composition of the power sources. To do this you need to be able to read the labels. Properly selected batteries will serve for a long time and with high quality.
11.06.2014
What is a battery
1. Classification
Batteries can be divided into three categories: lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride and alkaline.
①Lithium-ion batteries (also called Li-ion or LIB) are a family of rechargeable batteries in which lithium ions move from a negatively charged electrode to a positively charged electrode when discharging and back again when charging. Chemistry, efficiency, cost and safety vary depending on the type of LIB. Unlike the original disposable lithium batteries, lithium-ion electrochemical cells use lithium compound plates instead of pure lithium metal as the electrode material.
Lithium-ion batteries are the most common in consumer electronics. They are one of the most popular types of rechargeable batteries for portable electronics, featuring the highest amount of energy per unit weight, no memory effect, and little energy loss when not in use. In addition to consumer electronics, LIBs are also becoming increasingly popular for use in military and electric vehicles, as well as in the aerospace industry. Scientific research continually brings improvements to traditional LIB manufacturing technologies, with particular attention to energy quantity, service life, cost and intrinsic safety.
②Alkaline batteries are a type of primary cell battery dependent on the reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide (Zn/MnO2). Rechargeable alkaline batteries allow specially designed cells to be reused.
Compared to the zinc-carbon battery or zinc-chloride battery types, alkaline batteries have more energy per unit weight and a longer shelf life at the same voltage. Silver-zinc disk batteries have more energy and power, but also more cost, than alkaline batteries of the same size.
Alkaline batteries get their name from the alkaline electrolyte potassium hydroxide instead of the acid ammonium chloride or zinc chloride electrolyte in carbon-zinc batteries. Other types of batteries also use an alkaline electrolyte, but different active materials for the electrodes.
③3A Nickel Metal Hydride batteries, abbreviated NiMH or Ni-MH, are a type of rechargeable battery. They are very similar to nickel-cadmium cells (Ni-Cd). NiMH uses nickel metahydroxide (Ni-OOH) positive electrodes like Ni-Cd, but the negative electrode is made of a hydrogen-absorbing alloy instead of cadmium. A NiMH battery can have two or three times the power of a similarly sized Ni-Cd, and their amount of energy per unit weight approaches that of lithium-ion cells.
Typical energy density for small NiMH cells is approximately 100 Wh per kg, and for large ones about 75 Wh per kg (270 kJ). This is significantly higher than the usual 40-60 Wh/kg for Ni-Cd, and similar to 100-160 Wh/kg for Li-ion. NiMH have a specific energy per unit volume of approximately 300 Wh/L (1080 MJ/m3), which is significantly higher than NiCd batteries at 50-150 Wh/L, and approximately similar to Li-ion at 250-360 Wh/L. l.
NiMH batteries have replaced Ni-Cd in many ways, especially small rechargeable batteries. NiMH batteries come in the common AA size, with a nominal charge capacity (C) ranging from 1100 mAh to 3100 mAh at 1.2 V, measured at a full discharge rate of five hours. The useful discharge capacity is a decreasing function of the discharge rate, but at a discharge rate of approximately 1xC (full discharge within an hour), it does not differ significantly from the rated capacity. NiMH batteries typically operate at 1.2V per cell, which is slightly less than standard 1.5V cells, but most devices operate at this voltage.
About 22% of portable rechargeable batteries sold in Japan in 2010 were Ni-MH. In Switzerland in 2009, similar figures were approximately 60%. This percentage is falling every year due to the rise in Li-ion battery production: in 2000, almost half of all portable rechargeable batteries sold in Japan were NiMH.
One significant disadvantage of Ni-MH batteries is their high self-discharge rate; A Ni-MH battery loses 3% of its charge per week of storage. In 2005, low self-discharge (LSD) batteries were developed. LSD Ni-MH batteries self-discharge much more slowly, but this comes at the cost of reducing their capacity by about 20%.
2. Battery types
Table of standard battery sizes
|
Name |
Other names |
Form |
Voltage |
|
R6, R06, MN1500, MX1500, PC1500, AM3, UM3, UM-3, HP7, 15AC, 15A, E91, EN91, 815, AL-AA, ALAA, 7524, HR6, HR06, LR06, LR6, X91, PC1501, Mignon, Penlight, Double A, 2AA |
Cylindrical, length 50 mm, diameter 14.2 mm |
1.5 V |
|
|
LR03, LR3, LR03X, R03, R3, MN2400, MX2400, PC2400, AM4, UM4, UM-4, HP16, 24AC, 24A, 24G, EN92, E92, 824, ALAAA, AL-AAA, 7526, 4003, K3A, Micro, Microlight, Potlood, Penlight, Triple A, 3AAA |
Cylindrical, length 44.5 mm, diameter 10.5 mm |
1.5 V |
|
|
AAAA |
LR61, 25A, MN2500, MX2500, E96, EN96, GP25A, LR8D425, 4061, K4A, Quadruple A, Quad A, 4AAAA |
Cylindrical, length 42 mm, diameter 8 mm |
1.5 V |
|
LR14, R14, UM2, UM-2, MN1400, MX1400, PC1400, 14AC, 14A, E93, EN93, 814, ALC, AL-C, 7522, AM2, HP11, Baby, Mignon |
Cylindrical, length 46 mm, diameter 26 mm |
1.5 V |
|
|
LR20, R20, R20MA, R20P, MN1300, MX1300, PC1300, UM1, UM-1, SUM-1, AM1, 13AC, 13A, E95, EN95, 813, AL-D, 1250, 7520, HP2, HR20, Mono, Goliath |
Cylindrical, length 58 mm, diameter 33 mm |
1.5 V |
|
|
PP3, 1604AC, 1604A, 1604AC, 522, EN22, A1604, AL9V, AL-9V, 9-Volt, Radio Batty, 6am6, 6um6, 006p, 6LR61, PC1604, PL1604, L522, 1604LC, U9VL-FP, K9V, S006 , S-006, 6F22, Nine Volt |
Rectangular, height 48.5 mm, length 26.5 mm, width 17.5 mm |
9 V |
|
|
CR17354, 5018LC,CameraBattery, CR123, LR123, VL123, 123A, CR123A, EL123A, EL123AP, EL123AP-2, RL123, RL123A-1, RL123A-2, DL123A-1, DL123A-2, SF123A, SF 12-BB, K123A, RCR-123A, 23-155, CR-123APA |
Cylindrical, length 34.5 mm, diameter 17 mm |
3 V |
|
|
DLCR2, DLCR2B, RLCR2, KCR2, EL1CR2, RLCR2-L, CR-2, 5046LC |
Cylindrical, length 27.5 mm, diameter 16 mm |
3 V |
|
|
LR1, LR01, 910A , MN9100, 4001, E90, KN, 810, 23-023, AM5, UM5,UM-5, SUM5, Lady Battery |
Cylindrical, length 30.2 mm, diameter 12 mm |
1.5 V |
|
|
4LR61, 7K67, 4018, 539, KJ, 4AM6, 4UM6, 4UM-6, 1412A, 1412AP, 867 |
Square with beveled corner, height 48.5 mm, length 35.6 mm, width 9.18 mm |
6 V |
3. Notes
①The voltage of all rechargeable batteries is 3.7V - 4.2V. If the batteries are connected in series, the total voltage remains 3.7V - 4.2V. (Note: TM11 includes 4 18650 batteries and its total voltage is 4.2V If it includes 8 CR123 batteries, the total voltage is 6 V. (Due to design limits, the TM11 cannot use RCR123 batteries)
②The voltage of all rechargeable batteries is 3V.
③The voltage of alkaline batteries is 1.5V, Ni-MH batteries are 1.2V.
④The brightness of the flashlight depends on the battery voltage.
⑤Battery type conversion: AA=14500, CR123A=16340, CR123A*2=18650。 (Note: 14500 Li-ion batteries are not applicable for our products, which are used with two AA batteries).
4. Battery types changes: AA=14500, CR123A=16340, CR123A*2=18650.
(Note: 14500 Li-ion batteries are not suitable for our products, which are used with two AA batteries).
Batteries are recognized as a necessary attribute of everyday life. Power sources are present in every home, making electrical equipment work: calculator, clock, flashlight, remote control, medical and cosmetic devices, children's toys, and so on. For their long-term and proper operation, it is important to follow the recommendations for battery selection, use and disposal.
What is a battery: device
The first direct current source was introduced in 1800 by Alessandro Volta. The galvanic cell, or battery, consisted of circles made of 2 different metals (electrodes), and pieces of fabric placed between them, soaked in a saline electrolyte solution.
This battery structure is called a “Volt Column”, and the unit of voltage is the Volt. The battery contains copper and zinc, and the solution is sulfuric acid.

However, there is a significant disadvantage of this design. When the zinc plate was dissolved, hydrogen bubbles formed on the copper plate, creating a barrier between its boundary and the solution. This polarization phenomenon had a negative effect on battery performance.
To eliminate it, an element invented by Leclanche was used. Graphite and zinc rods were placed in a container with ammonia solution. The first absorbed hydrogen due to a layer of manganese dioxide. At the same time, the performance of the carbon-zinc battery has improved.

Modern galvanic cells have the described design; a wide range of their varieties is presented on store shelves. However, they differ only in what their components are made of, which affects the performance and service life of the device.
The diagram of how the design works is identical for different types of batteries and is based on the generation of electricity during chemical reactions. It is shown in the picture.

The source of electrons is the anode. As a result of the action of the electrolyte and the oxidation reaction, elementary particles move along the conductor towards the cathode, performing work (lighting a light bulb, rotating an electric motor). Having reached it, the electrons participate in the reverse reduction reaction. The electrolyte acts as a medium for the transfer of ions. The circle is closed.
All reactions in a galvanic cell are irreversible, which makes it possible to distinguish it from batteries. Therefore, the battery is not charged, the electrodes are destroyed over time, and it “runs out.”
The first commercial manufacturer of voltaic cells was the Everready company in the USA, followed by Duracell.
Since their inception, batteries have undergone many improvements, which have affected their performance and service life.
Kinds
Batteries are classified depending on the material from which the components are made: anode, cathode, electrolyte. There is a difference in size, shape, and voltage output of the batteries.

The most popular are salt and alkaline (alkaline) food sources. Other types are less common due to high price, toxicity, and specific application.
Salt
Battery characteristics include low current output, short service life and shelf life. The electrodes inside the power source are made of manganese and zinc oxide and are connected by a salt bridge, which makes the design identical to the initial samples of the Duracell company.

However, improved zinc-manganese batteries are in demand due to their low price. How much a package costs depends on the number of batteries in it, the average price is 100 rubles for 4 pieces. The shelf life of the device is 2 years, at the end of which the capacity is typically reduced by up to 30-40%. At low temperatures, batteries often stop working.
The market offers products from Sony, Toshiba, Duracell and so on.

It is advisable to use them for devices with low consumption: watches, remote controls, scales.
Disadvantages include the risk that the battery will leak if left in the device for a long time unused. This is due to an increase in the active mass of the cathode and an increase in pressure on the electrolyte solution. Such processes, along with the decomposition of manganese dioxide and corrosion of zinc, increase the volume and pressure in the battery.
Alkaline (alkaline, alkaline)
Universal products are presented on the market by Duracell, FinePower, Energizer, Trophy and others.

The name is due to the constituent electrolyte - potassium hydroxide. The electrodes are zinc and manganese dioxide. The structure of an alkaline product is shown in the figure.

Compared to salt batteries, alkaline batteries have a longer shelf life (5 years) and greater capacity and power.
The advantages of the product include operability when exposed to low temperatures, reduced self-discharge rate. Due to the improved sealing, there is a low risk of battery leakage.
It is advisable to use alkaline products in devices with moderate load: radios, nightlights, toys, and so on.
The disadvantage of this type of battery is the gradual decrease in output voltage. The price of such products is higher than that of salt products.
Lithium

The battery design contains a lithium cathode separated from the anode by a separator and a diaphragm wetted with electrolyte.

The products can withstand intense current consumption for a long time. Powerful batteries have excellent characteristics: constant voltage, high energy density, long shelf life (up to 12 years) and operation, and temperature resistance. Lithium products are light in weight, do not leak, and can be charged.
It is advisable to use such batteries for devices with high energy consumption: cameras, flashlights, portable speakers.
Lithium products are recognized as the best, but are much more expensive than previous types of power sources.
Mercury

Inside the battery is a zinc anode and a mercury oxide cathode, separated by a separator and a diaphragm soaked in an alkaline solution of potassium hydroxide.

The power source is capable of functioning as a battery, but during cyclic operation its capacity decreases. This occurs due to mercury draining and droplets forming inside the product.
The advantages of the battery include voltage stability, high energy density and capacity, resistance to temperature changes, and a long shelf life (10 years).
However, the product has a number of significant disadvantages: expensive price, unsafe use (risk of inhaling mercury vapor during depressurization), and difficulties with disposal. For these reasons, batteries of this type are not popular.
Silver

In the power supply, the anode is zinc, the cathode is silver oxide, and the electrolyte is potassium or sodium hydroxide.

The batteries have good characteristics and a long period of storage and operation. They note high energy density and capacity (30-50% higher than lithium), voltage stability, and temperature stability.
The disadvantages of the power source include the expensive price.
Zinc air

Batteries of this type are produced by Power one, Rayovac, Duracell and others.
The anode in the power source is zinc, the electrolyte is a solution of potassium hydroxide or zinc chloride, and the cathode is a gas electrode.

The battery is characterized by high energy capacity. However, the disadvantage is the short service life due to the drying out of the electrolyte solution.
It is advisable to use batteries for hearing aids. To start the chemical reaction, before inserting the galvanic cell, it is important to remove the protective film from its surface and wait a minute.
Standard sizes
The classification of batteries is based on American standards, taking into account their size, type, model. Power supplies are designated AA, AAA, C, D, PP3, 3336, A23 and so on. They are shown schematically in the figure with dimensions indicated.

Batteries in everyday life are called, depending on their external features: finger batteries (the size of a finger), little fingers, “inch” (type C), “barrel” (D), tablets (disc).
Please note that product sizes may vary by 1-2 millimeters. The reason is a dense film that protects the battery from damage and external influences.
Finger (AA, R6, LR6, LR06)
This type of battery is considered the most common; it looks like a cylinder with a diameter of 13.5-14.5 millimeters and a length of 50.5 millimeters. In everyday life it can be called 2A, 2AA.

Rated voltage - 1.5V. Weight varies and ranges from 14-30 grams. To enhance performance, batteries are used, for example, lithium-ion (Li-Ion) format 14500. In this case, the voltage is 3.6 V, capacity 900 mAh.

It is advisable to use galvanic finger elements of this type in small equipment: remote controls, toys, watches, lanterns, and so on.
Littlefinger (AAA, R03, R3, LR03, LR3)
Cylindrical galvanic cells. The thickness of pinky batteries is less than that of finger batteries. In everyday life they may be called 3A.

The length of the cylindrical section is 44.5 millimeters, the diameter is 10.5 millimeters, the weight is about 12 grams, the voltage is 1.5 V. The capacity of the salt product is 500 mAh, the alkaline one is 1250 mAh, the battery is 300-1250 mAh.
Similar technical parameters are typical for power supplies 24A, MN2400, UM 4, HP 16, Micro, and so on.
Batteries are used in electronics that consume low current: remote controls, cameras, radios, and so on.
AAAA element (LR8, LR8D425, R8D425, LR61, E96, V4004, 25A)
Rarely used in small devices: light pointers, styluses for digital tablets, glucometers, and so on.

The voltage is 1.5 V, the mini battery length is 42.5 millimeters, diameter is 8.3 millimeters, capacity is 625 mAh. The A4 galvanic cell weighs only 6.5 grams.
C type (R14, CR14, LR14, 343, UM2)
The power supply is bulkier and heavier compared to previous battery sizes.

The length of the P14 is 50 millimeters, the diameter is 26.2 millimeters, and the weight is 37 grams. Battery voltage is 1.5 V, salt cell capacity is 1750 mAh, alkaline cell capacity is 3000-8200 mAh.
Rarely used due to the compactness and reduction in size of modern devices. Type C batteries serve energy-intensive electrical equipment: portable speakers and players, radios, hand-held spotlights.
D type (R20, LR20, 373, UM1, Mono)

The thick and long battery has a height of 61.5 millimeters, the diameter of the cylindrical part is 34.2 millimeters. The weight of a type D product is 66-141 grams, the voltage is 1.5 V. The capacity of the salt cell is 4 thousand mAh, the alkaline cell is 5500-16000 mAh.
It is advisable to use this battery format in devices that are electrically loaded: walkie-talkies, portable radios, voltmeters, hand-held flashlights, and so on.
Krone (6F22, 6LR61, 6LR61, 1604A, CR-9V, PP3, 522, MN1604, MX 1604)

The rectangular galvanic cell differs from others in its high voltage, which is 9V. The length of the battery is 48.5 millimeters, the capacity of the alkaline product is 625 mAh. The contacts are on one side, the power supply weighs 53 grams.
A square galvanic cell is used for devices that require high energy consumption: testers, device control panels, toys, shockers, and so on.
LR1(N)
The galvanic cell is used to power laser pointers, voice recorders, wireless doorbells, microphones, and so on.

It has a long shelf life (7 years) and is temperature resistant.
The height of the product is 29.7 millimeters, the diameter is 11.5 millimeters. The battery weighs 25 grams.
Pills
The round mini-battery looks like a tablet. They come in different sizes and shapes: small, larger, flat, convex.

They are also called a “dry” cell: in such batteries, the anode is silver oxide, the cathode is zinc, and the electrolyte is a paste-like saline solution.
The voltage in power supplies can vary depending on their type;
- 1.4 V - zinc air (PR);
- 1.5 V - alkaline (LR);
- 1.55 V - silver-zinc (SR);
- 3 V - lithium (CR).
Mostly the tablets are made of lithium with a voltage of 3 Volts (CR2016, CR2450). Galvanic cells of the CR2032 standard size are used to power volatile components (CMOS memory, clocks, most motherboards).

The designation of tablets among manufacturers differs significantly. Below is a table of correspondence between disc batteries for watches.

Based on the data, you can easily determine analogues from different manufacturers. For example, those for tablet 377 or 377a are V377, D377, LR66, LR60SW, LR626, LR626SW, L626E. The table shows the diameter and height of the element.
Such tablets are widely used for wrist watches. However, they are also used for calculators, hearing aids, sensors, and so on.
The correspondence of manganese-zinc clock power supplies is shown in the table.

Based on the data, it is possible to determine analogs to batteries AG1 (G1), AG10, AG6, and so on.
The following correspondence table identifies replacements for power supplies SR44, SR721W, SR521W and others.

Marking
All types of batteries are classified according to standards: American ones are well known. In Russia, the designations were developed by GOST, but they are rarely used in everyday life.

Depending on the materials used to manufacture the batteries, the following markings are used:
- R-salt;
- LR - alkaline;
- SR - silver;
- CR - lithium.
By the letter designations you can determine which class the product belongs to. For example, a CR123a battery is lithium. Products of this type may also bear the designation “Lithium”. Alkaline cells are labeled "ALKALINE".
The photo shows various sizes of alkaline batteries and Krona.

According to the approved designation system, the product body must contain characteristics of energy intensity, composition, size, type, voltage.

The information in the photo indicates that the battery is alkaline (LR), its capacity is 15 Ah, size is AA, voltage is 1.5 Volts.
Technical features
When choosing batteries, it is important to consider their technical parameters.
The main ones include:
- Voltage- the indicator varies depending on the type of batteries. For most batteries it is 1.5v, for lithium batteries the voltage is 3 V. Krona batteries with a voltage of 9V have increased power. Batteries also have a high rate, for example, 26650 with a voltage of 3.7 V and so on.
- Self-discharge- determines the loss of capacity during storage. Depending on this indicator, the expiration date is set on the batteries. The shortest period is typical for salt products (2 years), the longest - for lithium products (up to 12 years). Alkaline ones are stored for up to 5 years, mercury ones for up to 10 years. Temperature changes provoke self-discharge.
- Capacity- the parameter determines how much electricity is in the battery. The service life of the product depends on this characteristic. The smallest capacity is for popular salt and alkaline batteries (600 mAh). The highest figure is observed for products of type D (15000-18000 mAh).
Capacity and voltage parameters for various types of batteries are presented in the table.

How to distinguish rechargeable batteries from regular ones
When purchasing power supplies, you can choose rechargeable (battery) or regular. To do this, it is better to pay attention to the appearance of the product:
- The inscription “do not recharge” means that the device cannot be recharged. Otherwise, the indication "rechargeable" specifies the possibility of recharging.
- The batteries are marked with the designation of their type (Ni-Cd - nickel-cadmium, Ni-Mh - nickel-metal hydride, Li-Ion - lithium-ion).
- The price of regular batteries is cheaper than those with rechargeable capabilities.

Galvanic cells can be distinguished by their technical characteristics. If you measure a battery with a multimeter, a voltage value of 1.5 V indicates that this is a regular product, a parameter not higher than 1.2 indicates a battery. However, nowadays you can find rechargeable cells with a higher rating (1.6V).
How to choose the right one
In order not to make a mistake when choosing a battery, it is recommended to read the instructions for the device.
The document or the device itself must indicate the size of the suitable power supply.
When choosing a battery, you should consider the features of its type:
- Salt products are not suitable for powering high-power and medium-power devices (camera flashes, professional flashlights, etc.).
- Alkaline batteries are suitable for devices with low to moderate power consumption. However, they are not suitable for powerful lighting devices.
- Lithium batteries can be used for any device. However, for small equipment it is not advisable to use this type; it is permissible to get by with cheaper analogues.
The question often arises of how to choose a battery for your phone. These batteries are usually lithium-ion, so it is better to purchase a product labeled Li-Ion or Li-polymer. They do not require the device to be completely discharged, like older models.

After purchase, it is recommended to connect the phone to power for at least 20 hours. Next, it is advisable to completely discharge the device and charge it again (repeat at least 2 times). You can use recommendations on how to quickly drain the battery on your phone: launch several browsers, games, turn on a flashlight, camera, or use a special application for urgent discharge.
When using batteries, it is important to take the following precautions:
- do not burn them;
- do not disassemble;
- do not recharge products that are not intended for this purpose and are primary elements;
- Keep away from children - if swallowed, nutritional sources in tablet form may cause fatal internal bleeding.
Batteries are considered potentially hazardous devices for the environment, especially mercury ones. It is not recommended to throw away used products with other waste; it is advisable to hand them over to special collection points
For many devices, the voltage of a regular AA battery is not enough, and connecting several elements in series is not possible due to the small size of the electrical device. The way out of this situation is to use power supplies whose voltage is much higher. Most often, a Krona battery is used to power such devices, but if you need a source with a voltage of 6 volts, then you should install a Lithium 2CR5.
Contents
Technical characteristics of the 2CR5 battery
All 2CR5 batteries have the following characteristics:
- Voltage – 6v.
- Discharge current – 10 mA.
- Chemical type - Li-MnO2.
- Weight – 43 g.
- Capacity – 500-1300 mAh.
It has a fairly long service life and a minimal self-discharge rate. The product is also capable of operating at temperatures as low as minus 20 degrees. Thanks to these qualities, the power supply is ideal for installation in low-power devices that can be operated in various modes.
Analogue batteries 2CR5
This type of battery has few analogues. The following are fully compliant:
- DL245.
- EL2CR5.
- RL2CR.
In addition, you can replace it with an EN-EL1 battery. The product is a little longer and the voltage at the terminals is about 7 V, but if such excesses are not critical, then it can be repeatedly used instead of a standard battery.
Also, some home craftsmen assemble a battery from two CR123A elements connected in series, which in electrical parameters and size is almost identical to the device to be replaced.
Battery applications
The 2CR5 lithium battery is used in professional photographic equipment. The high power of the product allows it to be used in other devices with high power consumption. This source can also be used in modern sensor mixers and powerful light sources. The product can also be used for independent construction of various devices that require a voltage of 6 volts to power them.
Can a 2CR5 battery be charged?
If the 2CR5 is a battery, then it can be charged. You can identify such a battery by its labeling. The battery usually has a capacity designation, which is expressed in mAh. In order to restore the capacity of such a product, it is enough to apply a constant voltage of the required voltage to its contacts.
Special chargers operating from a 220 V network are good at “reanimating” dead 2CR5 batteries. The charger should be selected in such a way that there is a slot on its body in which you can install a battery of such an unusual shape.
Standard batteries cannot be charged, so if the device is equipped with a salt or alkaline battery, then after it is discharged, it should be replaced with the same product.
Popular manufacturers and their features
You can purchase a power source made both domestically and imported. Today, the most popular batteries are the following brands:
- Energizer. Batteries from this manufacturer have increased capacity, which allows them to be used much longer.
- Duracell. All batteries from this manufacturer are of high quality and performance, but the cost of the products is quite high.
- Panasonic. The 2CR5 battery from a well-known Japanese manufacturer of household appliances is distinguished by high quality and stable operation at low air temperatures.
- Varta. Very high quality batteries from a well-known European manufacturer. They have good endurance and allow you to use electrical devices for much longer.
- Maxell. The products are characterized by relatively low cost and decent quality.
- Space. Batteries from a domestic manufacturer have a standard voltage, capacity rating and good performance characteristics.
- Eveready. Good quality products.
- G.P. Products from a well-known Hong Kong manufacturer have good performance characteristics and a relatively low cost.
- Sanyo. Japanese manufacturer of high quality batteries, including the 2CR5 model.
If original products were purchased, then the elements of any of the listed brands will last a long time.
What to look for when purchasing
When purchasing a product, you should first pay attention to the type of battery. Only if you purchase a product with the designation 2CR5 on the product body, will it be possible to safely replace the battery. The same should be done when choosing an analogue.
When purchasing, you should also pay attention to the fact whether the battery is a battery or not. It is quite difficult to confuse, because the price of the products differs significantly.
You should refuse to purchase the product if there are dents, abrasions or other damage on its body.
The types of batteries, their sizes and shapes are completely different, so sometimes, when you get to the store, a person simply does not know what he needs. It is difficult to imagine modern life without batteries. They are found in all household appliances around us: watches, laptops, flashlights, electric photo frames, children's toys and remote controls.
All batteries are marked and differ in capacity, cost and appearance. When purchasing, you need to pay attention to many things so as not to purchase a low-quality battery. After all, such an element will last a very short time, and in some cases it may disrupt the functionality of the device. Let's find out what types of batteries there are, and also understand their features and characteristics.
These batteries have their own history of development. The battery as a voltaic cell became popular in the 1920s. But Georges Leclanche is considered its inventor - it was he who in 1867 created the prototype of the battery known to us. Of course, at that time the battery had a completely different look.
The Eveready company began mass-producing them for consumers. At first, the company's focus was on owners of radios, but soon the new product was appreciated by workers in mines, enterprises, and sailors.
In 1920, the well-known Duracell company appeared on the market and began producing various batteries, which were especially popular. They have become more compact, lighter and, most importantly, cheaper. They consisted of a graphite rod, manganese oxide and a zinc cup. The operating principle was based on the occurrence of an electrical impulse.
Due to the presence of a graphite rod, manganese-zinc batteries were sometimes called carbon-zinc batteries. Over the entire history of their existence, such batteries have been improved and have undergone many changes and innovations. At the moment they can be found in any store. And carbon batteries were replaced by others, as described below.
Kinds
There are different classifications of batteries: depending on the type, output voltage, size, composition. The buyer can buy all types of batteries.
Let us analyze the classification based on the materials that are included in their composition (anode, cathode, electrolyte).
They are easy to distinguish by price, because they are the cheapest. The companies represented on the market are Duracell, Sony, and Toshiba. They are advanced manganese-zinc batteries. It is advisable to use it in devices with low voltage consumption: watches, scales, remote controls.

They discharge quickly and cannot be recharged. During prolonged use, the galvanic cell may leak. At sub-zero temperatures, salt batteries stop working. Despite many shortcomings, this product is in demand on the market.
Alkaline or alkaline
How to choose a battery
You can get lost in the modern variety of types of batteries and their names. They all have different costs, which depend on the brand, the composition of the battery, its type and the power of the output voltage.
When purchasing, pay attention to the following details:
- Type of battery. If you need a watch battery, you might want to get by with a cheap salt battery. But if you don’t want to change it every six months, then take alkaline one. Buy lithium batteries for powerful devices.
- Best before date. All batteries are prone to self-discharge, only in salt batteries this is very noticeable, but in other types it is not. In any case, if you buy a new battery, it will last longer.
- The voltage you need. Disk galvanic cells are capable of delivering from 1.5 to 3 V. This is enough for the uninterrupted operation of a wristwatch or a small flashlight. Finger ones are capable of creating a voltage of 4-6 V.
- Manufacturing company. Sometimes it is better to pay for a brand than to repair a device due to a leaking battery. In addition, many companies provide a guarantee on their products. In this case, do not throw away the dated receipt and packaging.
Some batteries are marked “rechargable”: this means they can be recharged using.
Many equipment manufacturers write specifically which brands of batteries are suitable for the device. In this case, take the instructions with you and feel free to purchase the battery you need.




