ACT
WASHING PIPELINES OF FIRE FIGHTING INSTALLATIONS
G . _______________ “____”_________ 19__
Object name ________________
____________________________________
(power plant, substation)
We, the undersigned __________________________________________________
in the face ___________________________________________________________________
(representative from the customer, full name, position)
_________________________________________________________________________
And _______________________________________________________________________
(representative from installation organization, full name, position)
_________________________________________________________________________
have drawn up this act that the pipelines ___________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
(installation name, section number)
The operation of fire automatics installations means their use for detecting or extinguishing fires, as well as their maintenance and repair. When operating AUP, APS, a set of measures is carried out that ensure:
technically correct use of settings, i.e. application when detecting or extinguishing a fire, in extinguishing mode;
proper storage;
timely and high-quality technical maintenance in order to maintain the installation in good working order;
timely and high-quality repairs;
Maintenance is understood as a set of works that provides control technical condition, extending the service life. Maintenance activities are divided into four groups:
preparing the installation for use after activation or repair, including refueling and loading operations (replacement of triggered or damaged sprinklers, etc.);
technical condition monitoring;
prevention;
routine repairs in order to maintain the reliability and durability of installations.
Technical condition monitoring is carried out to assess the ability of installations to perform specified functions. This ability is assessed by values certain parameters. If the values of these parameters correspond to the passport values, the installation is considered to be in good condition.
In case of deviation from the norms, the installation is faulty, because it cannot provide satisfactory performance specified functions. Thus, monitoring the state of installations comes down to compiling true ones, i.e. measured at the installation, values, parameters with their nominal values. As a result of the comparison, a conclusion is drawn about the technical condition of the installation and the possibility of its further use.
Maintenance is divided into daily, monthly, quarterly, and annual. During daily maintenance the following scope of work is performed:
monitoring the condition of pipeline painting;
control over compliance with permissible distances (no more than two meters) from sprinklers to stored materials;
external inspection of control units (control and starting units, valves);
checking pressure gauges above and below the control and starting unit (the difference should not exceed 0.05);
operation of pumps and compressors in accordance with the instructions (certificates) of the manufacturers. The inspection results for each item are recorded in the “installation operation” log.
During monthly maintenance, daily maintenance work is carried out, as well as the following operations are performed:
inspection and preventive maintenance related to electrical equipment of installations;
checking the voltage of the main and backup power sources, inputs to automatic switches, inputs of automatic switches in the alarm circuit;
checking the functionality of electrical equipment circuits in remote and automatic modes;
inspection and preventive maintenance of all installation communications
checking pumps and their fittings, pressure - according to pressure gauges;
checking control and starting devices.
Quarterly maintenance includes monthly maintenance operations, in addition, the following work is performed:
checking the condition and fastening of the pipeline and sprinklers;
checking the operation of the ECM using a control pressure gauge;
turning the shafts of electric pump motors manually.
The annual includes quarterly maintenance activities and in addition to this:
leak testing of check valves and gate valves;
checking and certification of instrumentation within the time limits specified in the factory instructions;
replacement or repair of worn parts;
random check of water yield of sprinklers;
measurement of ground loop resistance.
In addition, there are types of maintenance work that must be carried out every 3 years. These include:
annual maintenance operations;
elimination of leaks in the system, repair of equipment fastenings;
touch-up of equipment;
repair of grounding devices;
measurement of installation drive insulation;
inspection of pumps, shut-off valves;
flushing the system.
AUP OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS.
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
Acceptance of the AUP for operation must be carried out by representatives of:
energy enterprises (chairman);
design, installation and commissioning organizations;
state fire supervision.
The commission's work program and acceptance certificate must be approved by the chief technical manager of the enterprise.
SECURITY MEASURES
When operating technological equipment of water fire extinguishing installations, personnel of energy enterprises must comply with the relevant safety requirements specified in PTE, PTB, as well as in factory passports and operating instructions for specific equipment.
During maintenance and repair of the automatic control system, when visiting a room protected by the automatic control system, the automatic control of a specific distribution pipeline in this direction must be switched to manual (remote) until the last person leaves the room.
Pressure testing of pipelines with water should be carried out only according to an approved program, which should include measures to ensure the protection of personnel from possible rupture of pipelines. It is necessary to ensure complete removal of air from the pipelines. Combining crimping work with other work in the same room is prohibited. If pressure testing is carried out by contractors, then the work is performed according to the work permit. The performance of these works by operational or maintenance personnel of the energy enterprise is documented in written order.
Before starting work, personnel involved in pressure testing must undergo workplace safety training.
There should be no unauthorized persons in the room during pressure testing. Pressure testing must be carried out under the supervision of a responsible person.
Repair work on process equipment must be carried out after removing the pressure from this equipment and preparing the necessary organizational and technical measures established by the current safety regulations.
PREPARATION FOR WORK AND CHECKING TECHNICAL CONDITION
FIRE FIGHTING UNITS
The foam fire extinguishing installation consists of:
source of foam supply (reservoir);
fire pumps (designed for taking and supplying solution into pressure pipelines);
suction pipelines (connecting the water source with fire pumps);
pressure pipelines (from the pump to the control unit);
distribution pipelines (laid within the protected premises);
control units installed at the end of pressure pipelines;
irrigators.
In addition to the above, based on design decisions, the following may be included in the fire extinguishing installation diagram:
a tank with a foaming agent solution for filling fire pumps;
a pneumatic tank to maintain constant pressure in the network of the fire extinguishing installation;
compressor for replenishing the pneumatic tank with air;
drain valves;
check valves;
dosing washers;
pressure switch;
pressure gauges;
vacuum gauges;
level gauges for measuring the level in tanks and pneumatic tanks;
other signaling, control and automation devices.
After completion of installation work, suction, pressure and distribution pipelines must be washed and subjected to hydraulic tests. The results of washing and pressure testing must be documented.
If possible, the effectiveness of the fire extinguishing installation should be checked by organizing extinguishing an artificial source of fire.
When flushing pipelines, water should be supplied from their ends towards the control units (in order to prevent clogging of pipes with a smaller diameter) at a speed 15-20% higher than the speed of the solution in case of fire (determined by calculations or recommendations of design organizations). Flushing should be continued until clean water appears steadily. If it is impossible to flush certain sections of pipelines, it is allowed to blow them with dry, clean, compressed air or inert gas.
Hydraulic testing of pipelines must be carried out under a pressure equal to 1.25 working pressure (P), but not less than P+0.3 MPa, for 10 minutes.
To disconnect the tested section from the rest of the network, it is necessary to install blind flanges or plugs. It is not allowed to use existing control units, repair valves, etc. for this purpose.
After 10 minutes of testing, the pressure should be gradually reduced to working pressure and a thorough inspection of all welded joints and adjacent areas should be carried out.
The pipeline network is considered to have passed the hydraulic test if no signs of rupture, leaks, drops are found in the welded joints and on the base metal, or visible residual deformations.
Pressure should be measured with two pressure gauges.
Flushing and hydraulic testing of pipelines must be carried out under conditions that prevent them from freezing.
It is prohibited to fill open trenches with pipelines that have been exposed to severe frosts, or to fill such trenches with frozen soil.
Automatic water fire extinguishing installations must operate in automatic start mode. During the period of personnel presence in cable structures (bypass, repair work, etc.), the start-up of installations must be switched to manual (remote) activation.
MAINTENANCE OF FIRE FIGHTING INSTALLATIONS
Persons responsible for the operation, overhaul and current repairs of process equipment of a fire extinguishing installation are appointed by the head of the energy enterprise, who also approves schedules for technical supervision and repair of equipment.
The person responsible for the constant readiness of the process equipment of a fire extinguishing installation must have a good knowledge of the design principle and operating procedure of this equipment, and also have the following documentation:
project with changes made during installation and commissioning of the fire extinguishing installation;
factory passports and operating instructions for equipment and devices;
this Standard Instruction and local operating instructions for process equipment;
acts and protocols for conducting installation and commissioning work, as well as testing the operation of technological equipment;
schedules for maintenance and repair of process equipment;
“Logbook of maintenance and repair of fire extinguishing installations.”
Any deviations from the scheme adopted by the project, replacement of equipment, additional installation of sprinklers or their replacement with sprinklers with a larger nozzle diameter must be previously agreed upon with the design institute - the author of the project.
To monitor the technical condition of the process equipment of the fire extinguishing installation, a “Logbook of maintenance and repair of the fire extinguishing installation” must be kept, in which the date and time of the inspection, who carried out the inspection, detected malfunctions, their nature and the time of their elimination, the time of forced shutdown and startup must be recorded. fire extinguishing installations, testing of the operation of the entire installation or individual equipment.
At least once a quarter, the chief technical manager of the enterprise must familiarize himself with the contents of the magazine against receipt.
To check the readiness and effectiveness of the AUVP, a complete audit of the technological equipment of this installation must be carried out once every three years.
During the inspection, in addition to the main work, pressure testing of the pressure pipeline is carried out and in two or three directions, washing (or purging) and pressure testing of distribution pipelines located in the most aggressive environment (dampness, gas contamination, dust) is carried out.
If deficiencies are discovered, it is necessary to develop measures to ensure their complete elimination in a short time.
Automatic fire extinguishing installations in accordance with the schedule approved by the head of the relevant workshop, but at least once every three years, must be tested (tested) according to a specially developed program with their actual commissioning, provided that this does not entail a shutdown of the process equipment or the entire production process. During testing on the first and last sprinklers, the water pressure and irrigation intensity should be checked.
Testing should be carried out for 1.5-2 minutes with the inclusion of working drainage devices.
Based on the test results, a report or protocol must be drawn up, and the fact of testing must be registered in the “Logbook of maintenance and repair of the fire extinguishing installation.”
Checking the operation of the AUVP or individual species equipment should be carried out during repair, maintenance of the protected premises and technological installation.
A special room must be allocated for storing spare equipment, equipment parts, as well as devices, tools, materials, instruments necessary for monitoring and organizing repair work of the AUVP.
The technical capabilities of the AUVP should be included in the operational plan for extinguishing a fire at a given energy enterprise. During fire drills, it is necessary to expand the circle of personnel who know the purpose and structure of the fire control system, as well as the procedure for putting it into action.
Personnel servicing AUVP compressors and pneumatic tanks must be trained and certified in accordance with the requirements of the Gosgortekhnadzor rules.
The person responsible for the operation of the process equipment of a fire extinguishing installation must organize training with the personnel allocated to control the operation and maintenance of this equipment.
In the premises of the AUVP pumping station, the following must be posted: instructions on the procedure for putting pumps into operation and opening shut-off valves, as well as circuit and technological diagrams.
Entrances to the building (room) of the pumping station and fire extinguishing installation, as well as approaches to pumps, pneumatic tanks, compressors, control units, pressure gauges and other equipment of the fire extinguishing installation, must always be free.
In an operating fire extinguishing installation, the following must be sealed in the operating position:
hatches of tanks and containers for storing water supplies;
control units, valves and manual taps;
pressure switch;
drain taps.
After the fire extinguishing system has been activated, its functionality must be fully restored within 24 hours.
Checking the water level in the tank should be carried out daily and recorded in the “Logbook of maintenance and repair of the fire extinguishing installation.” If the water level decreases due to evaporation, it is necessary to add water, if there are leaks, determine the location of damage to the tank and eliminate the leaks.
The proper operation of the automatic level gauge in the tank must be checked at least once every three months at positive temperatures, monthly at negative temperatures, and immediately in case of doubt about the proper operation of the level gauge.
Tanks must be closed to access by unauthorized persons and sealed; the integrity of the seal is checked during the inspection of the equipment, but at least once a quarter.
The water in the tank should not contain mechanical impurities that could clog pipelines, dosing washers and sprinklers.
To prevent water from rotting and blooming, it is recommended to disinfect it with bleach at the rate of 100 g of lime per 1 m of water.
The water in the tank must be replaced annually in the fall. When replacing water, the bottom and inner walls of the tank are cleaned of dirt and build-up, and damaged paint is restored or completely renewed.
Before the onset of frost in buried tanks, the gap between the lower and upper hatch covers must be filled with insulating material.
Once a quarter, the condition of the inputs, shut-off valves, measuring instruments and water intake well is checked.
Before the onset of frost, the fittings in the water intake well must be inspected, repaired if necessary, and the well insulated.
Before testing the pumps, it is necessary to check: the tightness of the seals; lubricant level in bearing baths; correct tightening of foundation bolts, pump cover nuts and bearings; connections of the pipeline on the suction side and the pumps themselves.
Once a month, pumps and other equipment of the pumping station must be inspected and cleaned of dust and dirt.
Each fire pump must be turned on at least twice a month to create the required pressure, which is recorded in the operational log.
At least once a month, the reliability of transferring all fire pumps to the main and backup power supply should be checked and the results recorded in the operational log.
If there is a special tank for filling pumps with water, the latter must be inspected and painted annually.
Once every three years, pumps and motors, in accordance with clause 5.1.5 of these Standard Instructions, must undergo an inspection, during which all existing deficiencies are eliminated. Repair and replacement of worn parts, checking of seals is carried out as necessary.
The pumping station premises must be kept clean. When not on duty, it must be locked. One of the spare keys must be stored on the control panel, as indicated on the door.
Once a quarter you need to check:
absence of leaks and deflections of pipelines;
the presence of a constant slope (at least 0.01 for pipes with a diameter of up to 50 mm and 0.005 for pipes with a diameter of 50 mm or more);
condition of pipeline fastenings;
no contact with electrical wires and cables;
condition of painting, absence of dirt and dust.
Detected deficiencies that may affect the reliability of the installation must be corrected immediately.
The pressure pipeline must be in constant readiness for action, i.e. filled with water and under operating pressure.
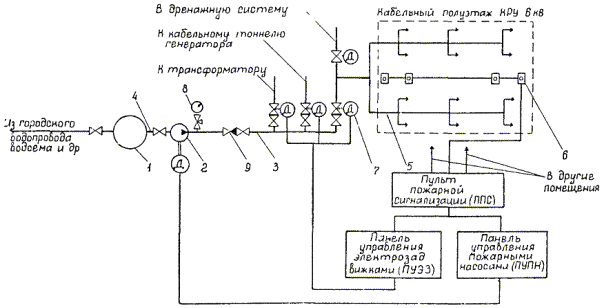
For automatic control systems of transformers and cable structures, steel fittings and electrified gate valves with automatic start of grade 30s 941nzh should be used in shut-off and start-up devices; 30s 986nzh; 30s 996nzh with a working pressure of 1.6 MPa, repair valves with manual drive brand 30s 41nzh with a working pressure of 1.6 MPa.
The condition of control units and shut-off valves, the presence of seals, and pressure values before and after control units must be monitored at least once a month.
Once every six months, the electrical circuit of the control unit should be checked with its automatic activation from the fire detector when the valve is closed.
The installation site of the control unit must be well lit, the inscriptions on the pipelines or special stencils (node number, protected area, type of sprinklers and their quantity) must be made with indelible bright paint and be clearly visible.
All damage to valves, valves and check valves that may affect the reliability of the fire extinguishing installation must be repaired immediately.
OPDR-15 sprinklers with a working water pressure in front of the sprinklers in the range of 0.2-0.6 MPa are used as water sprinklers for automatic fire extinguishing of transformers; For automatic fire extinguishing of cable structures, DV and DVM sprinklers with a working pressure of 0.2-0.4 MPa are used.
When inspecting switchgear equipment, but at least once a month, sprinklers must be inspected and cleaned of dust and dirt. If a malfunction or corrosion is detected, measures must be taken to eliminate it.
When carrying out repair work, sprinklers must be protected from plaster and paint (for example, with plastic or paper caps, etc.). Traces of paint and mortar found after repair must be removed.
It is prohibited to install plugs or plugs in place of faulty sprinklers.
To replace faulty or damaged sprinklers, a reserve of 10-15% of the total number of installed sprinklers should be created.
Putting the pneumatic tank into operation must be done in the following sequence:
fill the pneumatic tank with water to approximately 50% of its volume (check the level using the water gauge glass);
turn on the compressor or open the valve on the compressed air pipeline;
raise the pressure in the pneumatic tank to operating pressure (controlled by a pressure gauge), after which the pneumatic tank is connected to the pressure pipeline, creating working pressure in it.
Every day you should carry out an external inspection of the air tank, check the water level and air pressure in the air tank. When the air pressure decreases by 0.05 MPa (relative to the working one), it is pumped up.
Once a week the compressor is tested at idle.
Maintenance of the air tank and compressor, carried out once a year, includes:
emptying, inspecting and cleaning the air tank;
removing and testing the safety valve on a bench (if faulty, replace it with a new one);
painting the surface of the air tank (indicate the date of repair on the surface);
detailed inspection of the compressor (replace worn parts and fittings);
fulfillment of all other technical requirements stipulated by the factory passports and operating instructions for the pneumatic tank and compressor.
Disconnecting the pneumatic tank from the fire extinguishing installation circuit is prohibited.
The inspection of the pneumatic tank is carried out by a special commission with the participation of representatives of Gosgortekhnadzor, local bodies of the State Fire Supervision and the given energy enterprise.
The correct operation of pressure gauges installed on pneumatic tanks should be checked once a month; those installed on pipelines should be checked once every six months.
A complete check at the fire extinguishing installation of all pressure gauges with their sealing or branding must be carried out annually in accordance with the current regulations.
ORGANIZATION AND REQUIREMENTS FOR REPAIR WORK
When repairing process equipment of a fire extinguishing installation, one should, first of all, be guided by the requirements of the passport, the plant’s instructions for operating specific equipment, the requirements of relevant standards and technical specifications, as well as the requirements of this instruction.
When replacing a section of a pipeline at a bend, the minimum radius of the internal bending curve of steel pipes must be at least four outer diameters when bending in a cold state, and at least three in a hot state.
There should be no folds, cracks or other defects on the curved part of the pipe. Ovality in places of bending is allowed no more than 10% (determined by the ratio of the difference between the largest and smallest outer diameters of the bent pipe to the outer diameter of the pipe before the bend).
The difference in thickness and displacement of the edges of joined pipes and pipeline parts should not exceed 10% of the wall thickness and should not exceed 3 mm.
Before welding, the edges of the pipe ends to be welded and the surfaces adjacent to them must be cleaned of rust and dirt to a width of at least 20 mm.
Welding of each joint must be performed without interruption until the entire joint is completely welded.
The welded pipe joint must be rejected if the following defects are detected:
cracks extending to the surface of the weld or base metal in the welding zone;
sagging or undercuts in the transition zone from the base metal to the deposited metal;
burns;
unevenness of the weld seam in width and height, as well as its deviations from the axis.
In particularly damp rooms with a chemically active environment, pipeline fastening structures must be made of steel profiles with a thickness of at least 4 mm. Pipelines and fastening structures must be coated with protective varnish or paint.
Pipeline connections during open installation must be located outside walls, partitions, ceilings and other building structures of buildings.
Fastening pipelines to building structures buildings should be made with normalized supports and suspensions. Welding pipelines directly to metal structures of buildings and structures, as well as elements of process equipment, is not permitted.
Welding of supports and hangers to building structures must be carried out without weakening their mechanical strength. Sagging and bending of pipelines is not allowed.
Each pipeline bend longer than 0.5 m must have a fastening. The distance from hangers to welded and threaded joints of pipes must be at least 100 mm.
Newly installed sprinklers must be cleaned of preservative grease and tested with a hydraulic pressure of 1.25 MPa (12.5 kgf/cm2) for 1 minute. Average term The service life of sprinklers is determined to be at least 10 years.
I CONFIRM:
CEO
______________
________________
"___"____________ 2012 INSTRUCTIONS
ON THE OPERATION OF FIRE AUTOMATICS
____________ _________________ 1. AUTOMATIC FIRE FIGHTING. For fire extinguishing the following are provided:
-automatic installation of sprinkler water fire extinguishing with finely atomized water with installation of internal fire extinguishing valves on the supply pipelines to protect premises;
-internal fire water supply to protect service and auxiliary premises;
- equipment for a fire extinguishing pumping station.
To protect the premises of the shopping center, there is a water-filled sprinkler installation for automatic fire extinguishing with finely atomized water (water mist) using finely atomized water sprinklers CBS0-PHo(d)0.07-R1/2/P57.B3 "Aquamaster".
An automatic water sprinkler fire extinguishing installation consists of:
- supply pipelines;
- fire extinguishing station NS 70-65-3/100, which consists of
- pumping station module (MNS 70-65);
- module of two sprinkler control units MUU-ZS (MUU-3/100);
- module for connecting mobile fire fighting equipment.
Technical data of the fire extinguishing installation:
The “Potok-3n control device” manufactured by Bolid is used as a control device for the pumping station.
The "S2000M" remote control provides reception of signals, through addressable devices, from standard automatic addressable and manual call points, as well as technological sensors of fire extinguishing systems.
The system has an interface line, which is a two-wire communication line of the main structure with visual and audio indication of alarm and malfunction on the system devices. Possibility of programming devices for signaling the state of the fire extinguishing installation.
Additional installed modules allow you to protect technical premises with discrete smoke detectors, which are used for automatic control engineering systems; issuing information to light and sound annunciators, issuing sound alerts and documenting events. An indication module “S2000 BI isp.01” is installed in the duty personnel room, which allows for visual control of the operation of the automatic fire extinguishing pump station equipment.
A fire reservoir is used as a source of water supply.
To supply water to the pipelines of the sprinkler installation, booster fire pumps of the GRUNDFOS NB 50-257 type with a 30 kW electric motor (main and backup) are provided. Supply - 75 m3/h, with pressure - 81 m.
Operating principle of water fire extinguishing installation.
In standby mode, the supply pipeline (to the control units), supply and distribution pipelines are filled with water and are under pressure P = 0.5 MPa (50 m) created by the jockey pump.
Automation elements are in standby mode.
When a fire occurs in the protected premises, the temperature rises. An increase in temperature to 570C leads to the destruction of the glass flask of the sprinkler.
Opening the sprinkler leads to a drop in pressure in the supply and distribution pipelines.
The water pressure in the supply pipeline lifts the valve of the KS water-filled sprinkler valve of the "Bage" type.
When the valve of the control unit is opened, pressure alarms installed on the control unit generate a pulse to turn on the working booster pump for water supply, as well as a fire alarm (in case of failure smoke detectors earlier) and about the start of the installation.
If the working pump fails to create the design pressure Rcalc = 0.70 MPa, the backup pump is turned on and the working pump is turned off. Water flows through the open control unit through supply and distribution pipelines to the source of fire; the jockey pump is turned off.
Automatic start is carried out using the contacts of the "Potok 3N" device, which ensure the activation of the pumps of the fire extinguishing booster pumping station. Remote start of automatic smoke protection and warning people about a fire is carried out from manual fire detectors installed on evacuation routes. Manual start-up of booster pumps is carried out at the location of the equipment on the pump control cabinets.
After extinguishing the fire it is necessary;
- check the sprinklers and pipelines located in the combustion zone; if they fail, replace them;
- fill the distribution, supply and inlet pipelines with water;
- bring the opened control unit into working condition;
- bring automation elements into a state of control.
When operating the installations, the following rules must be followed:
1) repair work related to the installation and dismantling of equipment must be carried out in the absence of pressure in the unit being repaired;
2) cleaning and painting of pipelines located close to current-carrying elements is permitted only after removing the voltage from them and issuing a work permit;
3) persons involved in the work hydraulic tests, at the time of testing must be in safe places or behind a specially provided screen;
4) hydraulic and pneumatic tests of pipelines must be carried out in accordance with the approved instructions for testing pipelines;
5) lubrication of engines while moving, tightening bolts on moving parts of mechanisms is not allowed;
6) instructions and safety posters must be posted in the premises of control units and in the fire extinguishing station;
7) carry out repair work on electrical equipment after turning off the power supply;
8) when carrying out adjustment, repair and maintenance work, it is necessary to take into account that when installing an automatic fire extinguishing system, when the voltage is removed from any control cabinet (box), a voltage of 220V, 50 Hz may be present on electrical devices, terminal blocks of this device, since the automation control circuits are interconnected , and the remaining sources are not de-energized, therefore, before carrying out the specified work, it is necessary to carefully study the power supply circuit of the installation consumers, then de-energize necessary devices;
9) when performing work with electrical equipment, dielectric mats and gloves are required;
10) when performing repair work, portable lamps with a voltage not exceeding 42 V must be used;
11) all non-current-carrying parts of electrical equipment that may become energized as a result of insulation failure must be grounded (zeroed);
12) all work should be carried out only with working tools; the use of wrenches with extended handles, tool handles must be made of insulating material.
Operation of a fire extinguishing pump station.
1 To turn off fire pumps, make sure the fire is contained;
2 If the fire is extinguished or it turns out that a false alarm occurred
pump mode handles on pump control cabinets (main backup and jockey) to position “0”;
3 Call the service organization by phone ___________________;
To put the fire pumping station into standby mode, it is necessary to carry out the following actions:
1 All valves must be in the open position;
2 Turn off the power supply circuit breaker of the pumping station for 30 seconds;
3 Turn on the power supply circuit breaker of the pumping station;
4 Turn on all power circuit breakers in the electrical panel of the pumping station;
5 Move the pump mode handles on the pump control cabinets (main backup and jockey) to the “remote” position;
To check the operation of the pumps in manual mode (main backup and jockey), move to the “local” position. and briefly press the pump start button (green) on the control cabinet and, after making sure (1-2 seconds) that the pumps are working, briefly press the pump stop button (red) on the control cabinet. 2. AUTOMATIC FIRE ALARM AND SOUE
The automatic fire alarm system (AFS) is designed to detect the early stages of fire and smoke in retail and office premises ____________, turn on the voice warning system to organize the evacuation of people and turn on active fire protection(APZ).
The number of sound alarms (sirens), their placement and power provide the necessary audibility in all places of permanent or temporary residence of people.
The warning system is automatically turned on when a fire is detected in the building by a signal from the automated fire control system or automatic fire control system.
The APS exit point is located on the first floor in the security room. The fire department is equipped with a telephone connection. Security personnel work around the clock. On floors four to seven are located office rooms.
To organize the alarm system for the office part of the building, the following equipment is used:
- analog addressable smoke fire detector Z-051, according to NPB 88-2001* at least two detectors in one room (reacts to smoke in protected premises);
- manual addressable fire detector Z-041 (installed on evacuation routes);
- fire alarm control and receiving device "Z-101" (designed for connecting and monitoring fire alarm loops, for monitoring and controlling input and output units (Z-011. Z-022);
- addressable output block "Z-011" (designed to start the fire warning system, turn off the ventilation and air conditioning systems in case of fire, start the smoke removal system).
- linear smoke detector 6500R (responses to smoke in protected premises);
- the warning system uses equipment from the JEDIA company, which has all the necessary certificates.
Fire alarm station Z-101.
The fire alarm station is designed to receive signals from detectors, addressable devices and control technological equipment.
Information about the state of the fire alarm system is displayed on the display located on the front panel, which makes it possible to display information about the state of the system in real time.
Has 2 ring loops 250 addresses each.
Has an RS-485 output for connecting remote keyboards (up to 5 pcs.).
Z-101 is a fully completed fire alarm station with a full range of necessary functions.
The stations receive and process information from peripheral devices.
Each station has 5 programmable outputs, as well as a Fire relay and a Fault relay. There is also a 24V output and an output to an external siren.
Each station has a built-in printer with the ability to filter printed events.
Log of 999 events.
Addressable analogue fire smoke detector Z-051.
The Z-051 detector is designed to work with equipment of the Z-line series. The broadcaster is connected to an addressable loop (up to 250 addresses). Designed for optoelectronic detection of combustion products. Has a built-in indicator (LED). For internal use. The detector is programmed using the Z-511 address programmer.
The operating principle is photoelectric, working on the principle of light scattering.
Manual addressable fire detector Z-041.
Module Z -041 is designed to work with equipment of the Z-line series. Manual call point is installed on escape routes, staircases. When you press the glass, the microswitch is activated. Restoring the detector to an operational state is carried out using a key.
Insulator short circuit Z-011
Module Z -011 is designed to work with equipment of the Z-line series. The module is connected to an addressable loop (up to 250 addresses).
Purpose:
If a short circuit occurs in the loop, the short-circuited part of the loop between the two closest short-circuit modules is disconnected.
Has a built-in indicator (LED).
The number of modules in a loop is not limited.
Has no address.
Input module Z-021
Module Z -021 is designed to work with equipment of the Z-line series.
The module is connected to an addressable loop (up to 250 addresses).
Purpose:
- Designed to receive signals from external alarm sources.
- Contains an input with a 2 kOhm end-of-line resistor.
- Monitors the signal line for short circuit and open circuit.
- Has a built-in indicator (LED). Programming of the module is carried out using the Z-511 address programmer.
Application:
-Start buttons.
-Flame detectors with relay outputs.
-Flow switch, etc.
Output module Z-022
Module Z -022 is designed to work with equipment of the Z-line series.
The module is connected to an addressable loop (up to 250 addresses).
Purpose:
Designed to control external equipment.
Contains input feedback.
Receiving a "Fault" signal when the feedback circuit is closed without a "Fire" signal
Group of contacts for switching normally closed and normally open (N0-C-NC)
Has 2 built-in indicators (LED) Operation and Activation.
The module is programmed using the Z-511 address programmer.
Application:
Monitoring and/or control of various technological equipment
- fire-retarding valves,
- smoke exhaust hatches,
- pump boosters,
- ventilation systems, etc. Instructions for actions of duty personnel in the event of a fire alarm or malfunction
Upon receipt of the "FIRE" signal (activation of a smoothly changing tone sound signal and the red LED indicator "Fire" on the front panel of the device "Z-101"):
1. Report the incident to fire department(PCh-12) by phone 01 or _____________; report the address of the object where it is burning (the location of the fire), what the threat is (information about the fire is displayed on the LCD display - displaying the fact of a fire alarm and detailed information about the location of the fire).
2. Report the incident to the person responsible for fire safety __________________ by phone. __________________, to the head of the DPD _________________ by phone. ________________, to CEO __________________ by phone. ______________.
3. Check that the smoke removal, fire extinguishing, and fire alarm systems are turned on. If the warning system fails in automatic mode, manual call points should be used, as well as notifying service personnel and visitors by voice via radio broadcasting for the fastest and timely evacuation of people or transfer additional functions.
4. Open all door locks on the main and spare ones emergency exits from the building, the main power engineer (electrician) must de-energize the floor/building.
5. Send the security guard on duty or a member of the traffic police to meet the firefighters and escort them to the fire site.
The fire alarm condition can only be reset by manual reset (by pressing the "RESET" button on the front side of the Z-101 control panel). When receiving a “FAULT” signal on the fire alarm panel “Z-101” (an intermittent fault signal is issued to the built-in sounder and turns on the LED indicators on the front panel of the device):
1. View detailed information about the malfunction on the display (information about the malfunction is also printed on the built-in printer, namely the cause of the malfunction and the time the malfunction occurred). Try to switch the device by manual restart (by pressing the "RESET" button).
2. If normal operation of the device is not restored, it is necessary to reversibly remove some addressable loop devices from the equipment at the facility without reprogramming the entire system. For example, this could be a situation where it is necessary to switch off a faulty detector before the arrival service personnel. To do this, in standby mode, press the "menu" key and enter the password 111111. After entering the correct password, the operator menu will appear. To enter device shutdown mode, press "1". The following devices can be disabled: detectors, input and output modules, sirens. If at least one of these devices is disabled, the “Disabled” LED on the Device lights up. Shutdown information will be shown on the display.
3. Call a specialized organization to troubleshoot the problem. Tel._________________.
Mute sound (alerts):
The built-in siren is turned off manually by pressing the "Mute" key. At the same time, the “Sound Off” LED on the front panel lights up. If "Z-101" is in the sounding state or in the non-alarm monitoring state, the "Sound Off" LED on the front panel will go out.
Clearing alarm or fault information, restarting:
To clear fire alarm, supervision or fault information (main or backup power faults are indicated by LEDs, this is not shown on the display), press the "Reset" key by restarting the "Z-101". Information about disabling the device will be deleted from the display after canceling the disabling of the device (i.e., turning it on); information about the malfunction will be deleted after the malfunction is eliminated.
System testing:
On the information interface, press the "Test" (self-test) key to test on the LCD screen, the LEDs on the front panel light up and the annunciators are activated. After the self-test, the pending request state is automatically returned.
Key lock:
On the front side of the "Z-101" there is a lock with a key for locking and unlocking the keys. Turning the key to the left locks the keyboard. In this state, the operator can only mute the alert by pressing the Mute button. When the key is turned to the right, all keyboard functions are available.
Automatic and manual modes:
To switch manual/automatic modes, press the “manual/automatic” key and then enter the correct password 111111. If the Device is in automatic mode, the “automatic/manual” LED will light. When the device (Z-101) is in manual mode, the LED does not light up. The device (Z-101) in manual mode will not send any control signal automatically. In this case, control is carried out manually.
Entering a text description of the location of the addressable device (descriptor):
To enter location information in the administrator menu, press key 4 to exit to the descriptor input screen. When you enter the device address and press the "Enter" key, the display shows the available text information. To select the input mode, press the "Test" key. After selecting the input mode, enter the address (location) of the device.
More detailed information is given in the Operating Instructions for Network Addressable Analog Fire Alarm Panels of the Z-line Series, which is attached to this manual. 3. SMOKE EXHAUST SYSTEM
Fire safety ventilation systems are provided by:
- equipment of separate ventilation systems for premises of various functional purposes;
- installation of fire-retarding valves with standardized fire resistance limits in places where air ducts cross fire barriers (walls and ceilings);
- automatic shutdown general ventilation in case of fire and activation of the smoke ventilation system;
- thermal insulation made of non-combustible materials.
- air ducts of smoke removal systems and transit air ducts of ventilation systems are covered fire retardant composition.
The smoke removal system is turned on automatically when the fire warning system is started and the general ventilation is turned off (if the warning system does not work automatically, it must be started from manual call points). The instructions were compiled by ____________________ ANNEX 1.
Responsibilities of maintenance and operational personnel.
1.3.1. At the facilities, all types of work on maintenance and preventive maintenance, as well as on the maintenance of fire automatics installations must be carried out by the facility’s own specialists who have undergone appropriate training, or, under a contract, by organizations that have a license from the GPN management bodies to carry out installation, adjustment and technical maintenance of fire automatics installations.
1.3.2. At each facility, the following personnel must be assigned to operate and maintain fire automatic equipment in technically good condition by order of the manager:
- the person responsible for the operation of fire automatics installations;
- specialists who have been trained to perform maintenance and repair work on fire automatics installations (in the absence of an agreement with a specialized organization);
- operational (duty) personnel to monitor the condition of installations, as well as call the fire department in case of a fire.
1.3.3. Monitoring compliance with maintenance and repair regulations, timeliness and quality of work performed by a specialized organization should be entrusted to the person responsible for the operation of fire automatics installations.
1.3.4. The person responsible for the operation of fire automatics installations is obliged to ensure:
- compliance with the requirements of these rules;
- acceptance of maintenance and repair work in accordance with the schedule and work schedule under the contract;
- maintaining fire automatics installations in good working order and operational condition by carrying out timely maintenance and preventative maintenance;
- training of maintenance and duty personnel, as well as instructing persons working in protected premises on actions to take when the fire alarm system is activated;
- information to the relevant control bodies of the gas pumping station about all cases of failures and operation of installations;
- timely submission of complaints: to manufacturing plants - in case of delivery of incomplete, low-quality or non-compliant devices and equipment of fire automatics installations; installation organizations - upon detection of poor-quality installation or deviations during installation from the design documentation that were not agreed upon with the project developer and the state fire inspection body; service organizations - for untimely and poor quality maintenance and PPR installations and fire automatic equipment.
1.3.5. Maintenance personnel of the facility or a representative of a specialized
organizations are required to know the structure and operating principle of the fire automatics installation at the site, know and comply with the requirements of these Rules and the operating instructions for this installation.
1.3.6. Persons who discover a malfunction of the installations are obliged to immediately report this to the personnel on duty, and the latter to the person responsible for operating the system, who is obliged to take measures to eliminate the identified malfunctions.
1.3.7. The maintenance personnel of the facility or a representative of the service organization carrying out maintenance and repair of fire automatic equipment installations must carry out routine maintenance in deadlines and maintain the appropriate operational documentation given in the appendices to these Rules.
1.3.8. It is prohibited to turn off the fire automatics installations during operation, as well as to introduce changes to the adopted protection scheme without adjusting the design and estimate documentation, not approved by the territorial management body of the State Fire Department.
1.3.9. The administration of the facilities is obliged to ensure, during the period of maintenance and preventive maintenance work, the implementation of which is associated with the shutdown of installations, the fire safety of the premises protected by the installations by compensating measures, informing the management bodies of the State Fire Department and, if necessary, private security.
1.3.10. Operational (duty) personnel must know:
- Instructions for operational (duty personnel);
- tactical and technical characteristics of instruments and equipment of fire automatics installations installed at the enterprise, and the principle of their operation;
- name, purpose and location of the premises protected (controlled) by the installations;
- the procedure for starting the fire automatics installation in manual mode;
- procedure for maintaining operational documentation;
- the procedure for monitoring the operational state of the fire automatics installation at the facility;
- procedure for calling the fire department. APPENDIX 2.
Operation log
Fire automatic systems
(Form)
1.Name and departmental affiliation (form of ownership) of the facility equipped with a fire automatic system
(type of system, starting method)
Address_________________________________________________________________
Date of installation of the system, name of the installation organization
______________________________________________________________________
Fire automatic system type
______________________________________________________________________
Name of the organization (service) serving the system
______________________________________________________________________
Telephone_______________________________________________________________
2. Characteristics of the fire automatic system
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
(Name technical means, release date, start date of operation, next inspection period)
3. Fundamental wiring diagram fire automatic systems.
4. Results of hydraulic and electrical tests.
Date Test results Conclusion Signature 5. Acceptance and delivery of duty and technical condition of the system:
Date of acceptance and delivery State of the systems during the period of duty Name of the protected objects and type of systems from which the signals were received Last names, signature of the person who passed and took over the duty 6. Accounting for failures and malfunctions of fire automatic systems
No. Date and time of receipt of message Name
controlled
premises Character
malfunction Name and position of the person who accepted it Date and time the malfunction was eliminated Note 7.Accounting for maintenance and scheduled preventative repairs of fire automatic systems.
No. Date Type of system Controlled object Nature of work performed List of work performed Position, surname and signature of the person who carried out the maintenance Note 8.Checking the knowledge of personnel servicing fire automatic systems
№
Full name, position, work experience of the person being inspected Date of inspection Knowledge assessment Signature of the inspector Signature of the person being inspected 9.Accounting for the activation (shutdown) of fire automatic systems and information from fire suppression authorities
№
p/n Name of the controlled object Type and type of fire automatic system Date of activation (off) Reason for operation (off) Damage from fire Amount of saved valuables Reason for operation Date of GPN information 10.Instruction of technical and operational personnel on safety precautions when working with fire automatic systems.
№
p/n Last name of the person being instructed Position held by the person being instructed Date of the briefing Signature of the person being instructed Signature of the person who conducted the briefing APPENDIX 3.
Message
about the activation (failure) of the fire automatic system (sent to the territorial office of the State Fire Service)
1.Name of the enterprise and its address
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
(type of ownership)
2.Date of activation or shutdown_____________________________________________
3. Characteristics of the controlled premises___________________________
______________________________________________________________________
4. Reason for activation or shutdown __________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
5.Type of control panel or fire extinguishing system
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
6. Number of triggered sprinklers and detectors
______________________________________________________________________
7. Efficiency in detecting or extinguishing a fire of system fire automatic equipment__________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
(worked on time, late, etc.)
8. Estimated fire damage
______________________________________________________________________ 9.Rescued material assets due to the presence and timely operation of the fire automatic system_____________________________________________
(amount, thousand rubles)
10.If the system fails, indicate the reasons for the failure
______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ((last name, signature of the official) "_________"_________________________ 20_____ APPENDIX 4.
Work regulations
for the maintenance of fire extinguishing systems, fire and
security and fire alarm system.
Regulations
maintenance of water fire extinguishing systems
List of works Frequency of maintenance by the enterprise operation service Frequency of maintenance by specialized organizations under contract option 1 Frequency of maintenance by specialized organizations under contract option 2
Visual inspection components system (technological part - pipelines, sprinklers, check valves, dosing devices, shut-off valves, pressure gauges, pneumatic tank, pumps, etc.; electrical part - electrical control cabinets, electric motors, etc.), on no damage, corrosion, dirt, leaks; strength of fastenings, presence of seals, etc. Daily Monthly Quarterly
Monitoring pressure, water level, operating position of shut-off valves, etc. Daily Monthly Quarterly
Monitoring the main and backup power sources and checking the automatic switching of power from the working input to the backup input and back The same The same The same
Checking the operability of the system components (technological part, electrical part and signaling part) The same Same Same
Maintenance work Monthly Quarterly Quarterly
Checking system functionality in
manual (local, remote) and automatic modes Same Same Same
Flushing of pipelines and changing water in the system and tanks Annually Annually Annually
Insulation resistance measurement electrical circuits Once every 3 years Once every 3 years Once every 3 years
Hydraulic and pneumatic testing of pipelines for tightness and strength Once every 3.5 years Once every 3.5 years Once every 3.5 years
Technical examination of system components operating under pressure In accordance with the standards of Gosgortekhnadzor In accordance with the standards of Gosgortekhnadzor In accordance with the standards of Gosgortekhnadzor Regulations
maintenance of fire alarm systems
External inspection of the system components (control panel, detectors, sirens, alarm loop) for the absence of mechanical damage, corrosion, dirt, fastening strength, etc. Daily Monthly Quarterly
Monitoring the operating position of switches and switches, the serviceability of the light indication, the presence of seals on the receiver - control device Same Same Same
Monitoring the main and backup power sources and checking the automatic switching of power from the working input to
reserve Weekly Same Same
Checking the functionality of the system components (control panel, detectors, sirens,
measurement of alarm loop parameters, etc.) Same Same Same
Preventive maintenance Same Same Same
Checking system functionality Same Same Same
Metrological verification of instrumentation Annually Annually
Measurement of protective and working grounding resistance Annually Annually Annually
Regulations
maintenance of smoke protection systems
List of works Frequency of maintenance by the facility operation service Frequency of maintenance by specialized organizations under contract option 1 Frequency of maintenance by specialized organizations under contract option 2
External inspection of the system components (electrical part of the remote control panel, electrical panel of the floor valve of the local control panel, actuators, fans, pumps, etc.;
signaling part - receiving and control devices, alarm loop, detectors, sirens, etc.) for absence of damage. Corrosion, dirt, strength of fastenings, presence of seals, etc. Daily Monthly Quarterly
Monitoring the operating position of switches and switches, light indication, etc. Same Same Same
Monitoring of the main and backup power sources and automatic switching of power from the working input to
backup and back Weekly Same Same
Checking the functionality of the system components (electrical parts,
signaling part) Same Same Same
Checking system functionality in manual (local, remote) and automatic modes Same Same Same
Metrological verification of instrumentation Annually Annually
Measurements of resistance of protective and working grounding The same The same The same
Measuring the insulation resistance of electrical circuits 1 time every 3 years 1 time every 3 years 1 time every 3 years Download the operating instructions for fire alarm systems
VII. MONITORING COMPLIANCE WITH STANDARDS, RULES AND SAFETY REQUIREMENTS DURING OPERATION OF ASPS (ASPS) 36. Responsibility for organizing the operation of ASPT (ASPS) is assigned to the managers of facilities that are protected by fire automatic equipment.
37. In the process of a detailed inspection of the ASPT (ASPS), a representative of the State Border Service authorities checks the availability of the necessary technical documentation for the installation, analyzes its condition, conducts an external inspection and performance monitoring.
38. Requirements for operational technical documentation for ASPT (ASPS).
38.1. For each ASPT (ASPS), an order or instruction must be issued for the enterprise (organization), appointing:
the person responsible for the operation of the installation;
operational (duty) personnel for round-the-clock monitoring of the operating condition of the installations.
38.2. For each ASPT, operating instructions must be developed for those responsible for the operation of the installation and for the personnel servicing this installation, taking into account the specifics of the protected premises, approved by the management of the enterprise and agreed upon with the organization performing maintenance and repair of the ASPT.
The person responsible for the operation of the ASPT must promptly inform the local State Fire Service authorities about failures and operation of the installations.
38.3. Operational (duty) personnel must have and fill out the “Installation Failure Log” (Appendix 33).
38.4. An enterprise that carries out maintenance and repair of fire protection equipment must have a license from the State Fire Service of the Ministry of Internal Affairs for “Installation, adjustment, repair and maintenance of fire protection equipment and systems.”
Maintenance and repair may be carried out by site specialists with appropriate qualifications. In this case, the procedure for carrying out maintenance and repair work must comply with these methodological recommendations.
Restoring the functionality of ASPT or ASPS after its operation or failure should not exceed:
for Moscow, St. Petersburg, administrative centers of autonomous entities consisting of Russian Federation- 6 hours;
for other cities and towns - 18 hours.
38.5. An “Agreement for maintenance and repair of automatic fire extinguishing installations” must be concluded and valid between the operating organization and the enterprise performing maintenance and repair.
38.6. The control room premises must contain instructions on the procedure for the duty dispatcher to act upon receiving alarm signals.
38.7. Acceptance of ASPT for maintenance and repair must be preceded by a primary inspection of the installation in order to determine its technical condition.
The initial examination of the ASPT should be carried out by a commission, which includes a representative of the State Fire Service bodies.
Based on the results of the ASPT inspection, a “Certificate for the initial inspection of automatic fire extinguishing installations” (Appendix 34) and a “Report for the work performed on the primary inspection of automatic fire extinguishing installations” (Appendix 35) should be drawn up.
38.8. For an installation accepted for maintenance and repair, after concluding the contract, the following must be filled out:
passport of the automatic fire extinguishing installation (Appendix 36);
logbook for recording maintenance and repair of automatic fire extinguishing installations (Appendix 37). It must record all maintenance and repair work, including quality control. One copy of this log must be kept by the person responsible for operating the installation, the second - in the organization performing maintenance and repair. The log must also indicate the safety briefing of personnel performing maintenance and repair responsible for operating the installation. The pages of the magazine must be numbered, laced and sealed with the seals of organizations servicing ASPT and carrying out maintenance and repair;
maintenance and repair schedule (Appendix 38). The procedure for maintenance and repair of ASPT, as well as the period for eliminating installation failures, must comply with these methodological recommendations. The list and frequency of maintenance work must comply with standard ASPT (ASPS) maintenance regulations (Appendices 39-43);
list of technical equipment included in ASPT and subject to maintenance and repair (Appendix 44);
technical requirements defining the performance parameters of ASPT (Appendix 45).
38.9. The enterprise must have the following technical documentation:
ASPT initial examination report;
act on the work performed on the primary inspection of ASPT;
maintenance and repair agreement;
maintenance and repair schedule;
technical requirements defining the performance parameters of ASPT;
list of technical equipment included in ASPT and subject to maintenance and repair;
call log;
ASPT technical inspection report;
project at ASPT;
passports, certificates for equipment and instruments;
list of installed equipment, components, devices and automation equipment;
passports for charging installation cylinders gas fire extinguishing;
installation operating instructions;
maintenance and repair work log;
duty schedule of operational (duty) personnel;
log of duty acceptance by operational personnel;
log of weighing (control) of cylinders with fire extinguishing composition of gas fire extinguishing installations.
38.10. All necessary documentation for the ASPT (or copies thereof) must be kept by the person responsible for the operation of the ASPT.
39. During an external inspection of the ASPT and the premises protected by it, it is necessary to verify compliance with the project:
characteristics of the protected premises and its flammable load;
modifications of sprinklers of fire extinguishing installations, methods of their installation and placement;
cleanliness of sprinklers;
pipelines of installations (the use of pipelines of fire extinguishing installations for hanging, attaching, connecting equipment that is not related to fire extinguishing equipment is not allowed);
light and sound alarm located in the control center;
telephone connection of the dispatch center with fire department enterprise or locality.
40. In the process of monitoring compliance with norms, rules and safety requirements during the operation of ASPT, it is necessary to check their performance and conduct tests (without releasing fire extinguishing agent), confirming the installation of the main signals and commands.
41. Features of monitoring water and foam fire extinguishing installations during operation
41.1. When conducting an inspection of the technical condition of water and foam fire extinguishing installations, it is necessary to be guided by GOST R 50680-94 "Automatic water fire extinguishing installations. General technical requirements. Test methods", GOST R 50800-95 "Automatic foam fire extinguishing installations. General technical requirements. Test methods" and requirements of these rules.
41.2. During the inspection of water and foam fire extinguishing installations, the following should be checked:
41.2.1. Condition of sprinklers (in places where there is a danger of mechanical damage, sprinklers must be protected by reliable fences that do not affect the irrigation map and the distribution of heat flows).
41.2.2. Standard sizes of sprinklers (within each distribution pipeline (one section) sprinklers with outlet openings of the same diameter must be installed).
41.2.4. Availability of a supply of sprinklers (must be at least 10% for each type of sprinklers installed on distribution pipelines, for their timely replacement during operation).
41.2.5. Protective coating of pipelines (in rooms with a chemically active or aggressive environment they must be protected with acid-resistant paint).
41.2.6. Availability of a functional diagram for tying control nodes (each node must have a functional diagram piping, and in each direction - a plate indicating the operating pressures, protected premises, the type and number of sprinklers in each section of the system, the position (state) of the shut-off elements in standby mode).
41.2.7. Availability of devices on tanks for storing an emergency supply of water for fire extinguishing purposes, eliminating the consumption of water for other needs.
41.2.8. Availability of a reserve stock of foaming agent (a 100% reserve stock of foaming agent must be provided).
41.2.9. Providing the pumping station premises with telephone communication with the control center.
41.2.10. The presence at the entrance to the pumping station premises of a sign “Fire extinguishing station” and a constantly functioning light board with a similar inscription.
41.2.11. Availability of clearly and neatly executed pumping station piping diagrams posted in the pumping station premises and schematic diagram fire extinguishing installations. All showing measuring instruments must have inscriptions about working pressures and permissible limits of their measurements.
41.2.12. Duration of installation testing (testing of water and foam fire extinguishing installations during their operation should be carried out at least once every 5 years).
install plugs and plugs to replace broken or faulty sprinklers, as well as install sprinklers with anything other than the specified project documentation, melting temperature of the castle;
store materials at a distance of less than 0.6 m from sprinklers;
use the pipelines of fire extinguishing installations for hanging or fastening any equipment;
connect production or plumbing equipment to the supply pipelines of the fire extinguishing installation;
install shut-off valves and flange connections on supply and distribution pipelines;
use internal fire hydrants installed on the sprinkler network for purposes other than fire suppression;
use compressors for purposes not related to ensuring the operability of the installation.
42. Features of monitoring gas fire extinguishing installations during operation
42.1. In the process of monitoring the UGP during operation, it is necessary to:
carry out an external inspection of the installation components for the absence of mechanical damage, dirt, fastening strength, and the presence of seals;
check the working position of shut-off valves in the incentive network and launch cylinders;
check the main and backup source power supply, check the automatic switching of power from the working input to the backup one;
control the quantity of waste fuel by weighing or pressure control (for centralized UGP - the main and reserve quantity of waste fuel, for modular UGP - the number of waste fuel and the availability of its stock);
check the functionality of the installation components (technological part, electrical part);
check the operation of the installation in manual (remote) and automatic modes;
check the availability of metrological verification of instrumentation;
measure the resistance of protective and working grounding;
measure the insulation resistance of electrical circuits;
check the availability and validity period of the technical certification of the components of the UGP operating under pressure.
42.2. Control and testing of the UGP must be carried out without releasing the fire extinguishing agent according to the methods set out in GOST R 50969-96.
42.3. Control of the mass (pressure) of the state gas pump, control of the gas pressure in the incentive cylinders must be carried out within the time limits established by the TD at the UGP, with a note in the log. The requirements for GOS and propellant gas used when refueling (pumping) the UGP must be the same as for the initial refueling.
42.4. Fire extinguishing stations must be equipped and maintained in a condition consistent with design decisions.
42.5. If during operation of the UGP, its operation or failure occurs, the operability of the UGP must be restored (filling with GOS, propellant gas, replacing modules, squibs in launch cylinders, distribution devices etc.) in a timely manner and appropriate entries were made in the journal.
In the case of using GOS from the UGP stock, it must be restored simultaneously with the restoration of the UGP’s operability.
43. Features of monitoring aerosol fire extinguishing installations during operation
43.1. When inspecting objects protected by UAP, it is necessary to monitor compliance with a number of regulatory requirements.
43.1.1. The requirements of the maintenance regulations for the inspected UAP must not be lower than the requirements of the “Standard Maintenance Regulations for Aerosol Fire Extinguishing Installations”.
43.1.2. If mechanical damage is possible at the installation site of the GOA, then they must be fenced.
43.1.3. The installation locations of the GOA and their orientation in space must correspond to the project.
43.1.4. The GOA must have seals or other devices confirming its integrity.
43.1.5. The combustible load of the room protected by the UAP, its leakage and geometric dimensions must correspond to the design.
43.1.6. There should be no flammable materials on the surface of the GOA and in the area affected by the high-temperature aerosol jet.
43.1.7. Electrical wires intended to supply an electrical impulse to the GOA starting device must be laid and protected from thermal and other influences in accordance with the design.
43.1.8. The GOA reserve must correspond to the project.
43.1.9. Light and sound alarms must be in working order in the protected premises and in the duty post premises.
43.1.10. There must be instructions for maintenance personnel located in the protected premises on actions to take when the aerosol fire extinguishing installation is activated.
44. Features of monitoring modular powder fire extinguishing installations during operation
44.1. The list and frequency of maintenance work are determined in accordance with the regulations drawn up by the developer of the MAUPT based on the technical documentation for the components. The requirements of the maintenance regulations for a specific MAUPT must be no lower than the requirements of the standard maintenance regulations (Appendix 42).
44.2. The GPN checks the availability of entries in the registration log of maintenance and routine repairs of the MAUPT in accordance with the regulations and checks the maintenance of the passport of the pressure vessel (if its availability is necessary, in accordance with PB 10-115-96).
44.3. Additionally, representatives of the GPN conduct an external inspection of the MAUPT in accordance with clause 34.5 of these recommendations.
45. Features of monitoring fire alarm systems and automatic fire extinguishing installations during operation
45.1. When checking the organization of operation of the substation and AUP, a representative of the state fire control authorities must:
make sure that there is an order (instruction) from the facility administration to appoint a person responsible for the operation of installations and personnel for maintenance and operational round-the-clock monitoring of the substation and automated control system;
acquainted with technical documentation(project, working or as-built drawings, acts of acceptance and commissioning of installations, passports for instruments and equipment, operating instructions for installations, maintenance schedule, list of routine maintenance, maintenance log and installation malfunctions, job descriptions for maintenance and operating personnel, program and methodology for complex testing of installations);
check the ability of the duty (operational) and maintenance personnel to work with alarm control panels (boards), as well as their knowledge of the procedure for checking the operability of installations and actions when detectors and devices are triggered;
carry out technical condition monitoring, check the performance of the PS and AUP;
check the availability and serviceability of telephone communication with the fire station or control panel of the facility.
45.2. When monitoring the technical condition, conduct an external inspection of the equipment (fire detectors and their sensitive elements, protective nets and glass must be cleaned of dust). Check the presence of seals on the elements and assemblies to be sealed.
45.3. The orientation of the PI flame must correspond to the design.
45.4. When checking performance, the GPN representative must:
make sure that the detectors are triggered and the corresponding notifications are issued to the control panel and control signals from the control panel;
verify the functionality of the PS loop along its entire length by simulating a break or short circuit at the end of the PS loop, and also check the serviceability of the start-up electrical circuits;
make sure it works control panels, as well as control devices together with peripheral devices (sounders, actuators).
45.5. Checks according to clause 45.4 must be carried out by persons responsible for operating the systems.
OJSC "SIBNEFT-NOYABRSKNEFTEGAZ"
TERRITORIAL OIL PRODUCTION PROJECT
"KHOLMOGORNEFT"
I N S T R U C T I O N
on the operation of the water system
fire extinguishing equipment UPSVG-2 TsPPN-2.
Noyabrsk
2003
OJSC "SIBNEFT - NOYABRSKNEFTEGAZ"
TERRITORIAL OIL PRODUCTION PROJECT “KHOLMOGORNEFT”
APPROVED I APPROVED
Chairman of the trade union committee Head of TPDN
TPDN "Kholmogorneft" "Kholmogorneft"
___________ O.F. Yushko _______
S.Yu. Rusakov
"" _______2003 "___" ________ 2003
Head of PCH-130 OGPS-9
THEM. Miroshnichenko
"__" __________2003
I N S T R U C T I O N
on the operation of the water system
fire extinguishing equipment UPSVG-2 TsPPN-2.
I.General situation.
This instruction has been developed on the basis of the “Fire Safety Rules in the Russian Federation” (PPB 01-03) and the “Fire Safety Rules in oil industry» PPBO-85.
1.1. The head of the workshop, by his order, appoints someone responsible for the safe operation of the water fire extinguishing system.
1.2. The person responsible for technical operation regularly carries out inspections, checks and tests according to the schedule, together with the service organization of the entire water fire extinguishing system.
II. Purpose and device of water extinguishing.
2.1. The water fire extinguishing system is designed for external extinguishing of buildings and installation structures, as well as for supplying water to the tank farm for cooling the tanks by irrigation in the event of an oil fire in them.
2.2. The installation consists of a ring pipeline with fire hydrants designed by Doroshevsky in the amount of 13 pieces, located along the perimeter of the UPSVG and the tank farm and connected to the PPD system using valves No. 551/1, 551/2, 557, 558, valve units for supplying water along directions.
2.2.1. The water fire extinguishing system is dry pipe, laid above ground with heat traces. On fire water supply At high turning points, valves are installed to release air, and at low points, vents are installed to release water.
2.2.2. Block box for fire pumps – pumps K 100/65 – 2 pcs., for supplying water from fire fighting pumps – 1.2 to the fire ring.
2.2.3. The water supply, fire hydrants, fittings are thermally insulated along with heat traces with mineral wool mats.
2.2.4. All RVS-5000 are equipped with a stationary wall cooling unit, consisting of an irrigation ring and a supply dry pipe. The dry pipe is connected through a valve to the ring fire water pipeline. The irrigation ring consists of four parts; water is supplied to each part through a separate supply dry pipe. In addition, a dry pipe was installed to cool the tank walls from mobile equipment through the GM-80 connecting heads.
III. Preparing the water fire extinguishing system for operation.
3.1. When preparing the water fire extinguishing system for operation, it is necessary to check the position of manual and electric valves:
3.1.1. Valves connecting the water fire extinguishing system to the water supply system No. 550, 551/1, 551/2, 552 must always be open.
3.1.2. Electric valves No. 554, 555, 558 and valves on bypass lines No. 553, 556, 557 must be closed.
3.1.2. Fire ring valves Nos. 560, 561, 562, 563, 564, 565, 566, 567, 568 must be open.
3.1.3. All water supply valves for cooling tanks must be closed:
RVS-5000 No. 1 - No. 569/1-572/1, 569/1d-572/1d;
RVS-5000 No. 2 - No. 569/2-572/2, 569/2d-572/2d;
RVS-5000 No. 3 - No. 569/3-572/3, 569/3d-572/3d;
RVS-5000 No. 4 - No. 569/4-572/4, 569/4d-572/4d.
3.1.4. Valves No. 1, 2, 4, 14 on fire fighting stations – 1, 2 must be open
3.2. Check the pressure in the PPD system, it should be no lower than 5 kgf/cm 2
IV. Putting the water fire extinguishing system into operation.
4.1. To put the water fire extinguishing system into operation, you must turn on the K 100/65 pump to fill the system with water.
4.2. The pressure in the system must be maintained at least 5 kgf/cm2 by regulating the flow through valves Nos. 554, 555, 558 at the point of connection to the pressure maintenance system.
4.3. In case of fire on the RVS-5000, open valves No. 569-572 of the burning and cooled tanks. If more intensive cooling is necessary, we connect the fire fighting equipment using the GM-80 connection heads and open the corresponding valves (No. 569d-572d) of the additionally cooled tank.
4.4 Additional cooling of the tanks is possible by connecting
to the nearest safely located fire hydrants (PG 1-10)
Share
|