The external fire extinguishing system must be in working order at any hour of the day or night and at any time of the year. To ensure its serviceability, fire hydrants, an important part of fire-fighting water supply systems, are regularly checked.
Main check points
Hydrants must always be in working order. IN winter time every year they need to be cleared of snow and insulated. Access to water intake facilities is provided at any time of the year. If fire hydrants are installed on the roadway, then during inspection or firefighting, the road section is fenced off by installing warning signs. Signs are placed on the facades of nearby houses so that they are clearly visible.
During the inspection the following is checked:
- condition of the hatch cover;
- is there water in the well or inside the riser;
- Is the hydrant working properly with the installation and switching on of the water pump;
- what condition is the valve in (tightness, ease of opening/closing);
- condition of the head, thread, rod square.
The main failures are associated with corrosion of parts, freezing in winter period, thinning and failure of the gasket. All this leads to water leakage and the inability to use the device. The checked hydrant is noted in the log, recording whether there are any malfunctions so that they can be eliminated in a timely manner.
Reception and initial examination
The hydrant undergoes the very first tests at the factory to receive a quality certificate. It must then be tested before being put into operation. When purchasing a hydrant, they check the documentation, which contains operating rules, a warranty card and information about the quality certificate. Can be ordered together with the main set of parts check valve, which will prevent groundwater from entering the hydrant cavity. Other necessary spare parts are also ordered.
Before commissioning, an external inspection of the equipment is carried out and its functionality is checked. Threads and exposed unpainted metal areas must be lubricated; there should be no cracks, chips, or traces of rust on the parts. It is prohibited to use water from a fire hydrant for purposes other than firefighting or testing.
Test report
In spring and autumn, hydrants are checked with external inspection and water release. IN different regions In Russia, inspection times may vary due to climate conditions. After each inspection, a report is drawn up.
The report indicates the date of inspection, inventory numbers of hydrants, and addresses of their location. Indicate the diameter and type of pipeline, network pressure (in meters), water yield (in liters per second) and the name of the organization that maintains water intake devices. The fire hydrant inspection report is drawn up in several copies, giving one copy to a representative from each organization participating in the inspection.

Tests should be carried out during hours of maximum load on the water supply network. A representative of the company servicing the water supply network, members of the fire brigade and a fire inspector are present during the tests. They draw conclusions about the compliance of hydrants with standards fire safety. The findings are displayed in the fire hydrant test report. At the end, the commission members put their signatures.
Audit log

In addition to the report, a fire hydrant inspection log is kept. The log is filled out after each check, including after the first check, which occurs before commissioning. The log contains columns for entering the date of inspection, recording faults, their causes, and methods of elimination, so that you can quickly determine the condition of the tested hydrant. The results of each inspection are certified by the signature of the executing person and the controller. A person appointed by the management of a water utility or other service that manages hydrants is responsible for maintaining the log.
Features of seasonal testing and possible problems
The fall inspection is scheduled for September or October. During this period, special attention is paid to the location of groundwater. On the eve of frost, the well must be dry and clean. If there are blockages, they are removed, an external inspection is carried out and the hydrant is insulated.
The spring inspection takes place in April or May. The insulation is removed, the operation of the hydrant is checked, and the access roads are inspected. Check the condition and location of the signs and use a tape measure to measure the distance from them to the hydrant. It must correspond to what is indicated on the signs. In the spring, fire hydrants are most often tested for water loss using a special measuring equipment– hydrotesters.
When inspecting fire hydrants, you may encounter a situation where the head and other metal parts are so rusty that they are dangerous to touch. In this case, it is better to avoid screwing on the column and note the condition in the report in order to eliminate the problem during scheduled repairs.
The well may fill with water if the gasket between the stand and the hydrant or between the valve and the seat is worn out.
Sometimes the drain hole becomes clogged, which also leads to the filling of the hydrant cavity and well with water.
In winter, if there is no insulation, parts of the hydrant may freeze, and the shut-off device may fail. It is especially dangerous to install hydrants in northern latitudes that are designed to operate in the milder European climate.
Why know water consumption
During operation, diameter water pipes may decrease due to limescale, which is gradually deposited inside. The water pressure in the network also changes, the efficient operation of pumps, and leaks appear due to corrosion. To find out how critical all these changes are, check the fire water supply.
First of all, they check networks located at the farthest distance from pumping station. Dead-end pipelines, pipes with the smallest diameter and the weakest pressure are also subject to inspection. Fire hydrants and taps located in enterprises with a high fire hazard cannot be tested for water loss.
Water loss testing takes place after preliminary agreement with water supply services in the presence of a representative of these services. Hydraulic tests must be carried out once every 5 years.
How to check fluid loss
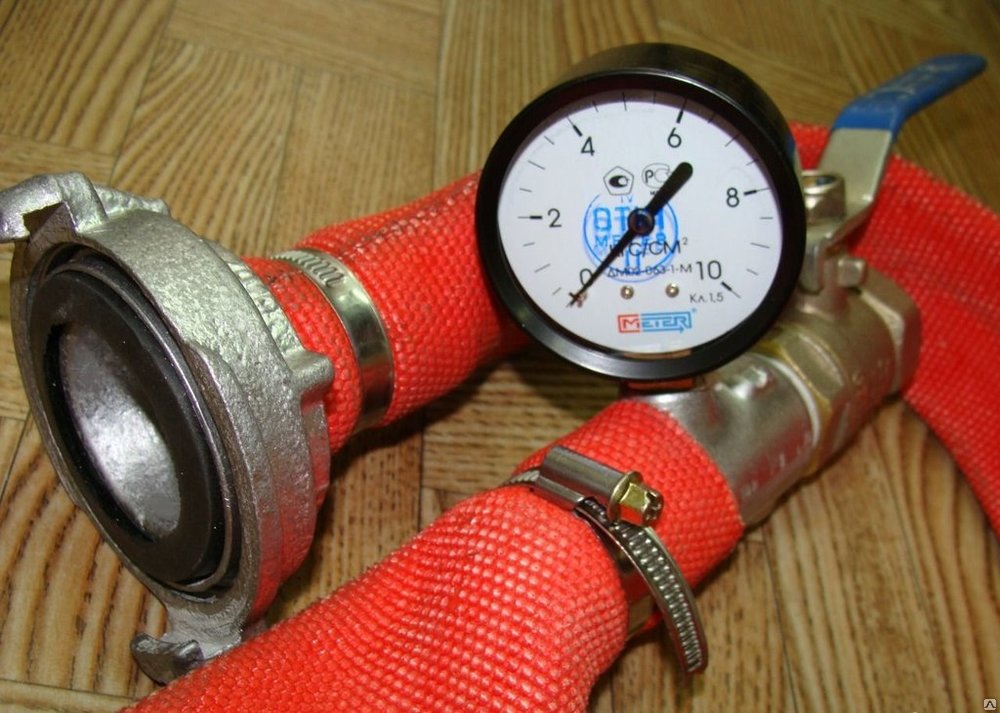

In the first method, fire hydrants are tested using a water meter consisting of a pressure gauge and a smooth tube. To determine the fluid flow, you need to screw the column onto the hydrant. Then connect a pressure gauge to one head of the column, and to the other a tube (smooth pipe) through which water will flow.
When meter installed, open the hydrant valve completely using a key, and unscrew the valve first from the pressure gauge side. His testimony is taken and recorded. Then open the valve on the tube side and record the pressure gauge readings again. Using the instrument readings and a special table, the water yield of the system is determined. The table shows the relationship between pressure, pipe diameter and fluid loss. Thus, knowing the diameter and pressure, you can determine how many liters of water are consumed per second and whether the consumption complies with fire safety standards.
DAILY ACT
fire hydrant inspections
Commission consisting of: _________________________________________________
(fire department representative)
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
representative of the municipal unitary enterprise "TZHKH" (TsVKiOS)_________________________________
drew up this act stating that “____”____________200_ a joint inspection of fire hydrants and reservoirs in the city of Gorodets, the city of Zavolzhye, JSC “ZMZ” was carried out
Fire hydrant no. | Nature of the malfunction |
||
Total:______________________________________________________________________________
Fire department representative:________________________________________________
Representative of the Municipal Unitary Enterprise "TZHKH" (TsVKiOS)_____________________________________________
fire hydrant acceptance
"_______"____________200__
We, the undersigned representative of TsVK MUP TZHKH (TsVKiOS) ________________________ and representative of PCh- ______________________, conducted a water loss test, checked the technical condition of SG No. __________________________________________________________________
(location, street)
PG No.______ is in __________________condition. Nature of service______________________________________________________________
Head of TsVK (TsVKiOS)_________________________
Chief of the Guard______________________________
Note: the act is drawn up in two copies
ACT of acceptance of a fire hydrant, DAILY ACT of inspection of fire hydrants and CONSOLIDATED ACT -drawn up in two copies
CONSOLIDATED ACT
"_____" _____________ 200___
We, the undersigned, are the representative of the fire department___________________________
On the one hand, and the person responsible for fire water supply _________________________________________________________, on the other hand, drew up an act stating that in the period from ______________________ to ______________________
200_____ a joint inspection of fire hydrants and reservoirs with water release was carried out.
Fire hydrants and reservoirs in the territory of ___________________________ were checked
Quantity |
||
Inspected fire hydrants and reservoirs | ||
Detected faulty fire hydrants and reservoirs | ||
Fixed fire hydrants and ponds | ||
Frozen fire hydrants discovered | ||
Heated fire hydrants |
Malfunctions of fire water sources were detected:
Nature of the malfunction | Troubleshooting |
||
Boss
PC-_________________________________________________
Responsible for p/p
Water supply of the city (object) __________________________________________
SAMPLE
INSTRUCTION
based on the results of the autumn and spring inspection of the external
Repair faulty fire hydrants
Clear access roads to fire hydrants No....
(Base: PPB – 01 – 03 p. 89)
At the location of the fire. hydrants, install three-dimensional illuminated signs or flat ones with a reflective coating (fluorescent).
(Basis: PPB – 01 – 03 clause 90; “Rules technical operation systems and structures of municipal water supply and sewerage" (PTE); No. 168 dated 12/30/99, clause 2.10.11)
Clean the manhole covers of the wells. hydrants No.... from earth, debris, ice, snow.
(Basis PPB – 01 – 03 clause 89; PTE No. 168 dated 12/30/99, clause 2.10.11)
Clean the SG wells from dirt, debris, snow
(Base: PPB – 01 – 03 clause 89; PTE No. 168 dated 12/30/99, clause 2.10.11; clause 2.10.12)
Pump water from the SG wells.
(Basis: PTE No. 168 dated December 30, 1999, clause 2.10.11; clause 2.10.12)
Carry out repairs and sealing of PG wells in order to prevent groundwater from entering them.
(Basis: PTE No. 168 dated December 30, 1999, clause 2.10.11; clause 2.10.12; clause 2.10.19)
Carry out scheduled preventive repairs and maintenance of fire hydrants and shut-off valves water supply network.
(Basis: PTE No. 168 dated 12/30/99, clause 2.10.19)
Conduct technical testing of fire hydrants for water loss.
(Base: PTE No. 168 dated 12/30/99, clause 2.10.17)
In the water supply section, create the necessary accounting documentation (logs)
(Basis: PTE No. 168 dated December 30, 1999, clause 2.10.51; clause 1.6.6)
QUESTIONS,
which must be reflected in the information addressed to the heads of administrations (facility managers) based on the results of the spring (autumn) inspection of the fire water supply of the area (facility).
Brief description of water supply (number of fire hydrants, reservoirs, piers, water towers, diameter of networks, including those that are faulty, including those that do not provide standard flow water for fire extinguishing purposes).
Analysis of faulty fire hydrants over the past 5 years.
Give 2-3 examples of fires where the water supply during fire extinguishing did not provide the required water consumption for fire extinguishing needs.
Reflect on the availability and condition of access roads to water sources (give examples).
Availability and condition of water source signs.
Show the role of water and waste management managers and enterprise managers in maintaining water sources in good condition.
Based on the results of the water supply tests, show compliance of the actual flow rate with the standard one.
Determine the need for water sources in settlements and facilities in the region (the required number of fire hydrants, reservoirs, piers, paved roads leading to them). Include this data as a proposal, including for waterless areas (villages).
Suggestions on what needs to be done to improve the maintenance of water sources in working order.
The certificate should include questions on the prospects for the development of water supply networks (replacement of networks, hydrants, repair of water towers, deepening and cleaning of ponds, installation of dams, construction of piers, construction of access roads to water sources).
The certificate should indicate whether water supply services have licenses to carry out repairs and other types of work, and what stage this work is at.
Note: 1. These questions must be reflected in the certificate in
mandatory.
2. Send copies of the letter with the report to SPT (3rd duty
EXTRACT FROM THE RULES(APPROVED BY ORDER OF THE GOSSTROY OF RUSSIA dated December 30, 1999 No. 168) TECHNICAL OPERATION OF SYSTEMS AND STRUCTURES OF PUBLIC WATER SUPPLY AND SEWERAGE
SECTION I. GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
Basic provisions
1.1.2. PTEs apply to the rights and responsibilities of operating personnel for the maintenance, provision of rational operating modes, acceptance and commissioning, control and accounting, repairs and elimination of damage and accidents on structures, equipment, devices and water supply and sewerage systems of the water and sewerage sector, as well as for the implementation requirements established to ensure proper sanitary and access control in protected areas.
1.1.4. PTEs are valid throughout the territory Russian Federation and are mandatory for the personnel of water and wastewater services organizations serving populated areas, regardless of their departmental affiliation, form of ownership and organizational and legal forms.
1.1.5. The operation of water supply and sewerage systems and structures is carried out by the water and wastewater services organization in accordance with the Rules for the use of public water supply and sewerage systems in the Russian Federation /3/ .
1.1.7. Organization of water and wastewater services when releasing water from the water supply system and (or) receiving waste water into the sewerage system organizes and conducts its activities in accordance with the “Rules for the use of public water supply and sewerage systems in the Russian Federation”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 12, 1999 No. 167 /3/.
1.1.9. Operation of water and wastewater services systems and structures is permitted only if the water and wastewater management organization has a license for licensed types of activities /6/.
1.1.25. The water and waste management organization must be specialized and have a staff of persons trained in accordance with methodological manual for certification of specialists in housing and communal services in Russia Area of activity "Operation external systems water supply and sanitation" /9/ and authorized to perform the required work, as well as the necessary material and technical base.
1.1.28. The functions of the water and waste management organization include:
a) administrative and economic and technical manual all divisions and enterprises under its jurisdiction;
b) development of plans for organizational and technical measures and systematic monitoring of their implementation to improve the reliability, efficiency and quality of service provision;
f) development and implementation of measures to prevent accidents and defects in work to improve the state of safety, industrial sanitation and labor protection, recording malfunctions, cases of injuries and accidents;
c) development of proposals for the development of water supply and sewerage systems.
1.1.29. For timely and clear resolution of issues of using water supply systems to extinguish fires and ensure maximum water yield of networks in areas of possible occurrence major fires The water and waste management organization, together with the fire service departments, is developing an interaction plan that takes into account local conditions.
Issues of interaction between the water and wastewater services organization and the State Fire Service (SFS) are regulated by agreements between the relevant water and wastewater services organizations and the territorial management bodies of the State Fire Service of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the Main Department of Internal Affairs, and the Department of Internal Affairs of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation
1.1.30. If accidents occur at structures, networks, equipment of water supply and sewerage systems, the water supply and sewerage organization immediately takes measures to quickly detect, localize and completely eliminate the accidents that have occurred and eliminate their consequences.
1.1.31. In case of emergency and other emergency situations inform the relevant government authorities, units of the State Fire Service, local government and State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision within the established time limits.
1.2. Operating personnel and their training
1.2.20. Systematic training of personnel is organized and personally supervised by the manager and chief engineer water and wastewater services organizations.
1.4. Responsibilities of administrative and technical personnel
1.4.1. The responsibilities of administrative and technical personnel are regulated by the “Regulations on the Unit”, which is approved by the management of the organization.
1.4.2. Administrative and technical personnel of the divisions of a manufacturing enterprise are obliged to:
a) manage the work of production and maintenance personnel,
b) provide workplaces with job and operational instructions, technological maps. Safety regulations, Fire safety regulations /16/, emergency response plans, instructions for civil defense in accordance with established legal provisions and familiarize each employee with them;
c) monitor the specified modes and level of reliability of the operation of structures and equipment and take the necessary measures in case of their violation;
d) draw up defective statements for current and major repairs of buildings, structures, equipment, work schedules and ensure their completion on time;
e) fill out requests for materials, equipment, spare parts, etc.;
f) monitor the correctness of keeping logs and records of the operation of structures and equipment, the availability of passports and other technical documentation, and promptly reflect in these documents changes that occurred during operation;
g) draw up reports on the operation of structures and equipment;
h) study the operation of individual structures, installations and equipment, make proposals for the introduction of new equipment, improvement technological processes, improving the designs of buildings and equipment, etc.;
i) organize technical training, drills in order to improve the qualifications of personnel;
j) conduct classes and safety briefings with operating personnel and constantly monitor compliance with safety regulations.
1.4.3. The "Regulations on the Division" must define:
1) purpose of the unit;
2) production functions;
3) interaction with related departments (shops, sections, laboratory, instrumentation, etc.);
4) criterion indicators of work quality;
5) composition and responsibility of performers;
6) responsibilities regarding the technological cycle;
7) responsibility for ensuring compliance with technological parameters (or regulations);
8) the quality functions they provide;
9) availability of technical documentation;
10) availability of documentation related to the quality of products (water, the composition of which is responsible for this unit);
11) department resources;
12) equipment and measuring instruments;
13) the procedure for conducting internal quality control checks (self-control procedure);
14) water quality parameters included in the unit’s area of responsibility;
15) duties and responsibilities established by these PTEs.
1.6 Technical documentation
1.6.2. Divisions and services of the water and waste management organization must be provided with copies of documents necessary for everyday use during the operation of structures, equipment, communications and control and automation equipment under the jurisdiction of these services.
1.6.6. The following are subject to permanent storage in the archives of water and wastewater services organizations:
c) operational diagrams of water supply and sewerage systems of the settlement as a whole or its isolated areas, indicating the location of all structures, main communications, means of regulation, automation and dispatching on a scale of 1:2000-1:5000. The diagram should contain a grid indicating the plate numbers;
d) tablets on a scale of 1:2000, made on a geodetic base, measuring 50x50 cm (1 km 2). All existing buildings, underground communications and structures in them must be marked on the tablets. When drawing communications of water supply and sewerage systems, the diameter, length, material and year of construction of the pipelines must be indicated; complete equipment and numbers of wells (chambers) with marks of the ground, pipe or tray; fire hydrants - emergency releases; subscriber connections and their registration numbers.
Notes:
3. Certificates of acceptance of structures, communications and equipment for operation must be accompanied by the following documents:
f) acts hydraulic tests communications and structures for strength and tightness;
g) test reports of fire hydrants for serviceability and water yield;
6. Complete set technical passports(maps) for structures, equipment, communications, units, handling equipment, etc.;
The product passport (card) must contain
a) name of the plant - manufacturer and year of manufacture of the product,
b) factory and inventory (local) number,
c) year of commencement of operation;
d) group and code according to the nomenclature of fixed assets;
d) technical characteristics, compiled on the basis of manufacturer’s data;
f) factory test report;
g) performance test data:
h) acts and data of inspection and repair, as well as protocols of tests carried out during repair;
i) reports of accidents that took place and materials from the analysis of the causes that caused the accident;
j) technical statistics data on operating time and load of the unit, etc.
l) wiring diagrams equipment;
l) installation diagrams for automating the operation of the unit:
m) list of spare parts;
o) basic adjustment dimensions and values for disassembly and assembly;
n) book value;
SECTION 2. WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS
2.1. Basic provisions
2.1.1. The main tasks of water supply systems operation services are:
a) ensuring uninterrupted, reliable and efficient work all elements of water supply systems - water intake structures, treatment facilities, water supply network, reservoirs and water towers, pumping stations.
2.10. Water pipelines and water supply network
General provisions
2.10.3. The operation of the water supply network is carried out by services, which, depending on the length of the network and the volume of work, can be used in the form of sections, departments, network services, and for especially large cities - in the form of independent production operational and emergency departments with division into regional operational sections of the water supply network.
Network supervision and maintenance
2.10.5. Supervision of the network condition should be carried out by inspecting pipelines and checking the operation of network structures and equipment.
Note: When carrying out this work, it is necessary to comply with the Rules /3/.
2.10.6. Based on the results of inspections and testing the operation of equipment, assessing the level of its reliability, measures are developed and carried out for the technical maintenance of the network, carrying out preventive, routine and major repairs.
2.10.7. To carry out operational work to monitor the condition and maintain the network, operational (preventive) and repair (emergency recovery) duty teams must be created, the number and composition of which are determined by local conditions.
2.10.8. All operational work on the network, with the exception of emergency response work, is carried out by teams along the routes established by the network operation plan, depending on the volume and nature of the tasks for the day.
2.10.9. Each brigade is daily given a patrol order prepared the day before, without which the brigade should not go to work. The brigade is given the necessary technical documentation(scheme of bypass routes, logs for recording detected defects on the network), vehicles, tools, equipment, drainage equipment, kit necessary funds on safety precautions, etc.
2.10.10. The work of operational teams is organized in accordance with job description, approved by the management of the water and wastewater services organization.
2.10.11. An external bypass and inspection of each route of the water supply network is carried out at least once every two months. At the same time, the following is checked:
a) the condition of coordinate plates and hydrant signs;
b) the technical condition of the wells, the presence and tightness of the covers, the integrity of the hatches, covers, necks, brackets, ladders, the presence of water in the well or its leakage by opening the well covers and clearing the covers of debris (snow, ice);
c) the presence of gases in wells according to instrument readings;
d) the presence of blockages on the route and network at the locations of wells, digging on the network route, as well as unauthorized work on the installation of connections to the network;
e) the effect of street water intakes.
Note: During an external inspection of the network line routes, people are not allowed to descend into the wells.
2.10.12. General preventive maintenance of network structures and devices is carried out alternately twice a year. In this case, the following work is performed:
a) in wells and chambers - cleaning and pumping water, breaking off ice in the necks, preventive maintenance of socket and flange connections, accelerating valve spindles, checking the operation of bypasses, adjusting the electric drive, inspecting plungers and other devices, checking the operation of fire hydrants with the installation of a stander on them, and also, if necessary, replacing brackets, repairing stairs, changing covers.
Note: Repair of fire hydrants must be carried out within 24 hours from the moment the malfunction is discovered. The water and waste management organization is obliged to notify the local unit of the State Fire Service of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia about the detected malfunction and the completion of the hydrant repair.
2.10.14. Preventive maintenance includes taking measures to protect devices and equipment on the network from freezing (installing and removing insulation, breaking off ice)
2.10.17. Checking the water supply network for water loss is carried out jointly by employees of the water supply and sewerage organization and the local unit of the State Fire Service. The water yield of a network section is determined using one of the recommended methods (volumetric, using a calibrated fire column, using water meter barrels). In accordance with the result of such a check, together with the local unit of the State Fire Service, a list of closed valves (gates) installed on the connections between the lines and on the bypass lines of pressure regulators is established under normal technical condition of the system, under various emergency situations, as well as when supplying water for fire extinguishing needs.
Scheduled preventative and major repairs, emergency response
2.10.18. Data from inspections and preventive maintenance with checking the condition of structures, the operation of equipment and devices on the network are used in compiling defect reports, developing design and estimate documentation and for the production of preventive and major repairs.
2.10.19. Scheduled preventative maintenance on the network includes:
A) preventive measures- washing and cleaning the network, ice chips, cleaning wells, etc. cameras from dirt, water pumping and other activities listed in the section “Supervision over the condition and maintenance of the network” of these PTEs;
b) renovation work- replacement of hatches, brackets, repair of the well neck, raising and lowering of hatches, etc.
2.10.20. Major repairs on the network include work on:
a) construction of new or complete or partial reconstruction of wells (chambers);
b) laying individual sections of lines with full or partial replacement pipes;
c) replacing hydrants, standpipes, valves, butterfly valves, plungers, other equipment or their worn parts;
2.10.28. The water supply and sewerage organization must notify the local unit of the State Fire Service and local bodies of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision about shutdowns in the water supply network associated with current or major repairs no later than one day before the start of work.
Notes:
1. About emergency shutdowns on the water supply network, the water and waste management organization must immediately notify the local unit of the State Fire Service and the local body of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision.
2. In case of work related to blocking streets, it is necessary to immediately inform the units of the State Fire Service.
Management and development of optimal operating modes for water supply and distribution systems
2.10.51. New pipelines and those connected to the existing system are marked on tablets stored in the technical department and on operational diagrams available in control rooms, indicating the wells (chambers), the equipment installed in them and assigning them the corresponding registration numbers. Passports are issued for new pipelines and structures.
Note : Fire hydrants have registration cards that indicate their number, address, installation date and all types of maintenance work performed.
LIST
guidelines for organizing control
for the state of fire-fighting water supply.
1. Federal Law“On fire safety.”
2. Law of the Nizhny Novgorod region dated October 26, 1995 No. 16-3“On fire safety.”
3. “Fire safety rules” (PPB-01-03).
4. “Rules for the technical operation of systems and structures of municipal water supply and sewerage No. 168 of December 30, 1999.”
5. ORDER of the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate No. 230 of 08/12/02.“On organizing and conducting inspections of fire-fighting water supply in Nizhny Novgorod and in the regions of the Nizhny Novgorod region.”
6. GOST 5.1763-72“Underground fire hydrants.” Requirements for the quality of certified products.
7. GOST 12.4.009-83“Fire fighting equipment for the protection of objects. Main types. Accommodation and service.” System of occupational safety standards.
8. GOST 12.1.004-91“Fire safety. General requirements" System of occupational safety standards.
9. GOST 1.601-95“Operational Documents”. Unified system design documentation.
10. GOST 12.3.006-75“Operation of water supply and sewerage facilities and networks. General requirements." System of occupational safety standards.
11. GOST 8220-85“Fire hydrants are underground. Technical conditions".
12. GOST 12.4.026-76“Signal colors and safety signs.” System of occupational safety standards.
13. SNiP 2.04.02-84"Water supply. External networks and structures.”
14. SNiP 3.05.04-85“External networks and structures of water supply and sewerage.”
15. NPB 201-96“Fire protection of enterprises. General requirements."
16. Yukhimenko V.G.“To the chief of the duty guard about fire water supply.” - M.: Stroyizdat, 1986.
17. Vorotyntsev Yu.P., Malakhov B.N.“To the inspector of the State Supervision Authority on fire-fighting water supply.” - M.: Stroyizdat, 1987.
18. Tudos A.V., chief specialist GUGPS Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia: (articles in the magazines “Firefighting”:
- “Because there is no water.”
- “Water supply in winter.”
19. Rules for the technical operation of water supply and sanitation systems in populated areas. Ministry of Housing and Utilities, 1979
20. Regulatory documents on water supply and sewerage services. Issue 1. Department of Housing and Communal Services of the Ministry of Construction of Russia, Research Institute of KVOV, Moscow, 1995.
21.GOST 25151-82"Water supply. Terms and definitions
1. Instructions for the maintenance and operation of firefighters
hydrants on water supply networks 2
2. Instructions for the maintenance and operation of fire reservoirs 5
3. GOST 8220-85 “Underground fire hydrants” 8
4. Water yield of the water supply network 16
5. Water consumption from the water supply network 17
6. The maximum number of ACs installed on the water supply system is 17
8. Daily inspection report of fire water supply 22
9. Fire hydrant acceptance certificate 23
10. Summary report of fire water supply inspection 24
11. Sample of drawing up an order based on the results of external inspections
fire water supply 25
12. Issues that need to be reflected in the information addressed to the heads
administrations (facility managers) based on the results of inspections
fire-fighting water supply of the area (facility) 26
13. Extract from the rules (approved by order of the Gosstroy of Russia No. 168
dated December 30, 1999) technical operation of systems and structures
public water supply and sewerage 27
14. List of guidance documents on organizing control
over the state of fire-fighting water supply 35
During fires, any rescue team arriving at the scene needs additional sources of the main argument in the fight against fire - water. Such a resource can be taken from a nearby body of water or by shuttling between the storage facility and the source of the fire. And if the first option is not available, and the second is unacceptable, then the fence is made from the water supply using a fire hydrant. His serviceability and ability to give required quantity cubic meters of liquid per second are important criteria in ensuring the safety of objects and people's health.
Photo from nenovosty.ru
What is a fire hydrant
First, it’s worth understanding the definition itself. This device is an outdoor or underground type structure. It is built into the water supply system and has valves for convenient connection to a special column (if underground) or directly to a fire hose (if external). They allow you to efficiently and quickly collect water and extinguish fire without wasting time using a special tank. The steam generator, regardless of its shape and location, must provide the necessary pressure, as well as be accessible and serviceable at any time of the year.
The need to check fire hydrants
Most water intake devices in Russia are underground and are located in special niches - fire-prevention wells, which have the unpleasant feature of filling with water.
This happens for several reasons:
- leaks in the SG housing if it is not closed correctly, as well as in the structure and pipes;
- location of the well in the lowlands.
This not only leads to corrosion and premature failure of equipment, but in winter it makes access extremely difficult and prevents the rapid elimination of fire. In addition, if the base of the PG is located above the freezing point of the soil, then exhaust valve and drain hole may freeze, causing deformation and malfunction.
Frequency of inspection of fire hydrants
The PPB requirements establish the need to inspect the steam generator twice a year, in weather specified by regulations and at above-zero air temperatures, in order to avoid the formation of ice.
- An audit is carried out in the spring and summer. At the same time, the insulation installed in the fall is removed, access roads are inspected, general condition PG.
- In the autumn-winter period, the well is checked and filled with water, insulation is carried out, and garbage is removed.
Nearby structures must have signs or any other signs indicating the location of the device, visible at night. Using a tape measure, the accuracy of the information printed on them is checked.
Photo from the website led-svetilniki.ru
The main purpose of the inspection is to check technical condition elements.
- The integrity of the hatch covering the well and the ease with which it opens. Also in winter, a special insulating box is required to protect against freezing.
- Technical condition of the well.
- The integrity of the SG housing, the absence of leaks and cracks leading to structural destruction.
- Ease of opening the shut-off valves, their tightness.
- Equipping the surrounding area and buildings with special signs indicating the location of the nearest water source.
Installation of a fire column
The operation of the fire hydrant is directly checked using a special column (KPA). It is installed in compliance with certain rules and precautions.
- The device is screwed onto the PG nipple until it stops and the thread is completely closed. In this case, the square of its unlocking device (central key) must connect to the groove in the valve. The operation is carried out with the outlet pipes of the column closed.
- The central key is turned half a turn to fill the KPA housing with water. The correctness of the actions performed can be determined by the sound flowing water and it and flowing out of the hydrant through the drain. This is necessary to prevent the so-called water hammer, which can lead to the destruction of the hydrant and tearing of the column from the thread with unpleasant consequences for others.
- After filling with water, the SG valve is allowed to open completely. You can start checking.

Photo from aliansm.ru
In the case of a ground-based structure, the same sequence of actions is performed with the exception of installing the column.
Testing hydrants for water loss
The main and most important parameter for the quality of operation of the described device is the amount of water it can deliver in a short period of time. It changes due to corrosion and deposits on the inner walls of water pipes. To determine the technical condition of such communications and the impact on the fire safety of the facility, a fire hydrant is checked for water loss. Formally, what is being checked is not its actual flow (this is, essentially, a tap), but the water supply network. This is especially true for:
- networks remote from the main highways (and therefore from pumps), where the required pressure may not be achieved;
- areas with small pipe diameters;
- old, renovated, dead-end, busy, long lines;
- water pipelines near structures with a high fire hazard.
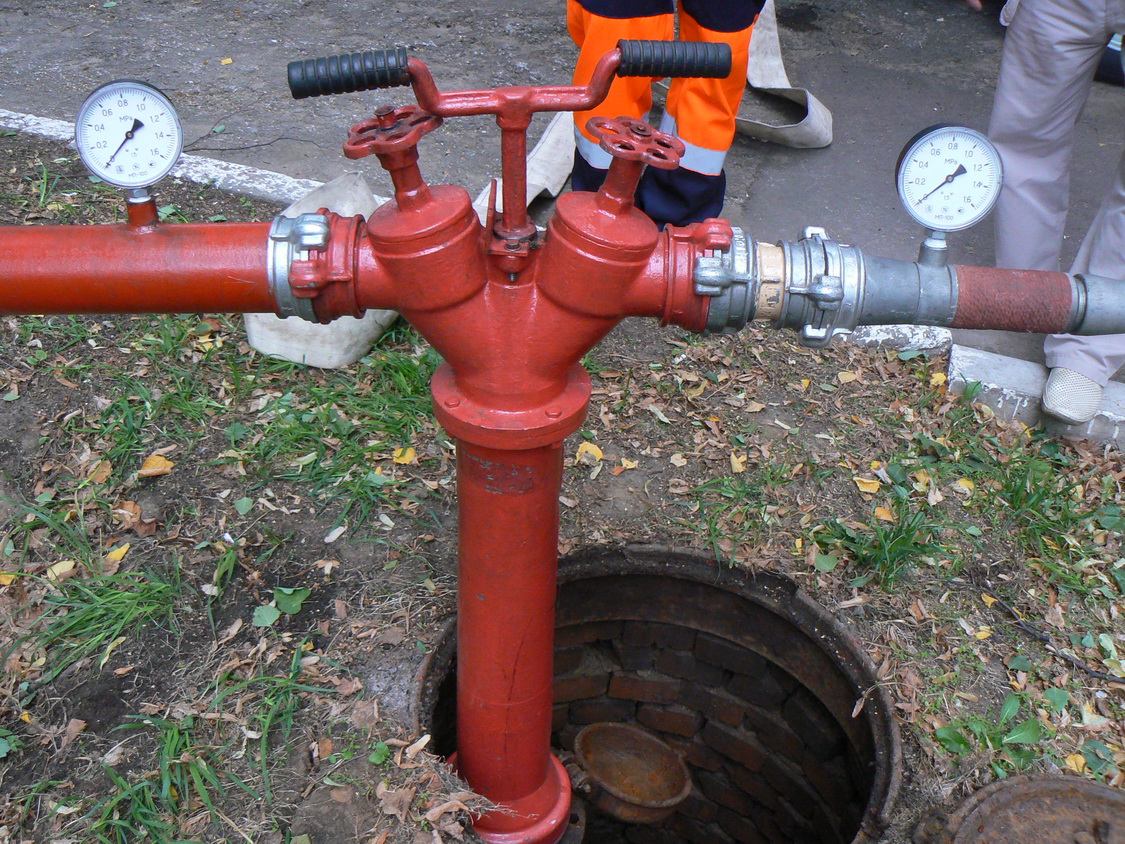

Photo from the website gov.cap.ru
The power of a fire hydrant is determined during the hours of maximum load on it. There are several ways to determine fluid loss.
- Volume. For this purpose, a large (≥0.5 m³) measuring tank and a stopwatch are used, which is used to determine the filling time. The actual consumption is calculated using the formula Qf = W⁄t, where W is the volume of the tank in liters, t is the time required to fill it in seconds.
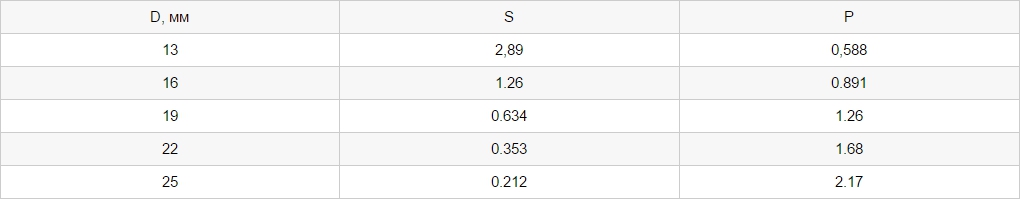
- Using a water meter. In this case, a regular fire nozzle is used, but with additional equipment in the form of a pressure gauge, as well as nozzles for measuring water loss at various diameters. Here the formula is used: Qф = P√H⁄√S, where P is the permeability of the nozzle, H is the pressure gauge readings, S is the resistance of the nozzle. The dependence of P and S on the trunk diameter (D) is shown in the table.
Alexey
In cities, they use to extinguish and localize fires. plumbing system. For this purpose, special devices are installed - fire hydrants.
It consists of a safety cap, nipple, O-ring and safety ring, stem and body. Height can vary up to 3m.
Based on the method of placement, a distinction is made between underground and above-ground. Such equipment is installed no further than 150 m from each other, no closer than 5 m from buildings and structures, and can be located on the roadway. The law requires regular inspection of fire hydrants.
A little about fire extinguishing agents
We watch the video, the scope of fire hydrants:
Fire crews use such objects both when directly extinguishing a fire and to fill the vehicle with water, while the PG acts as a pump. Above-ground devices are in many ways inferior to underground ones, but can also be used for other needs.
Why is the check performed?
According to the requirements of fire safety rules, hydrants are checked twice a year: in spring and autumn, at positive air temperatures.
 Based on the results, a corresponding act is drawn up. The most important thing is that the device provides an uninterrupted supply of water in the required volume at any time. A superficial inspection checks:
Based on the results, a corresponding act is drawn up. The most important thing is that the device provides an uninterrupted supply of water in the required volume at any time. A superficial inspection checks:
- Integrity of the hatch and cover;
- Serviceability of the hydrant body;
- Hydrants are checked using a column to see how easily the SG can be opened and closed, and very tightly;
- Valve tightness;
- Availability of signs
As a rule, the responsibility for the serviceability of the steam generator lies with the organization that controls the operation of the water supply and sewerage systems. Vodokanal works closely with fire department, in the event of a water supply shutdown, promptly informs them about it.
Let's watch the video about the need for verification work:
When extinguishing a fire high degree danger, the duty brigade helps the fire crew. Maintenance of the well cover in which the fire hydrant is located is carried out by the organization on whose territory it is located. It is necessary to constantly remove garbage, remove ice and snow, and provide free access to it.
When it is done legally
In April-May, with appropriate climatic conditions do a PG audit. At the same time, remove the cover, remove the insulation, inspect the condition of the access roads and the serviceability of the device. In September-October, the inspection of hydrants includes determining the location of groundwater, making insulation, removing blockages, and assessing the technical condition.
Signs indicating the distance and exact location hydrant. The plate must be made with fluorescent or reflective paints and be clearly visible. The reliability of the specified data is verified by measuring distances using a tape measure.
Testing hydrants for water loss
In accordance with fire safety requirements, it is important to maintain water supply sources in constant readiness for use to extinguish fires. For this purpose they are appointed responsible persons who maintain relevant documentation and control of activities:
- The GHG availability and audit log is filled out;
- Observe and note all changes in fire water supply;
- Information is provided in a timely manner to the heads of organizations on the territory of which the GHGs are located;
- Hydrants should be checked, repaired and replaced in a timely manner;
- Check the presence and serviceability of fire hoses, barrels and connecting elements.
In the spring, a technical inspection with water start-up is carried out during the daytime, when water consumption is maximum. Following the sign, they find the equipment, remove the insulation, and install fire pump, check the integrity of the connections, remove blockages and plugs, operability ball valve, integrity of the sleeve. Then the start-up is carried out and the water loss is measured using measuring equipment. Eliminate all identified faults. Check the compliance with the service range of nearby buildings. Special attention You should pay attention to filling out a fire hydrant inspection report.
We watch a video of how testing for water loss is carried out;
In the fall, the same activities are carried out as during the spring inspection. It is necessary to ensure that it is technically serviceable and, if found, correct it immediately. But besides that, you need to pump out groundwater if they are present in the hydrant riser, insulate them.
Since safety is important for everyone, you should not neglect it; you should listen to the advice of a specialist. It is necessary to keep the PG in working condition. Breakdowns are often associated with negative phenomena:
- Freezing in winter conditions;
- Filling the well with waste and groundwater;
- Drain hole clogged;
- Destruction caused by corrosion;
- Leakage due to a leaky gasket;
It should be noted that failure to comply with the requirements of the law entails liability. Supervision is carried out by the prosecutor's office, district authorities and the state fire inspectorate. Maintenance, repair and control is a very responsible matter, it is worth paying attention to important points:
- Inspection and installation of fire hydrants is carried out by organizations that have the appropriate approvals and licenses, which have quality equipment and trained specialists;
- Responsible organizations must ensure that they are freely accessible at all times.
There are several ways to test hydrants for water loss. You can use a measuring container and calculate the water consumption, knowing the volume and filling time. It is possible to make the necessary measurements using a fire nozzle with a pressure gauge, water meter or a special column.
The law provides for a unified type of drawing up a fire hydrant inspection report; you can obtain an established sample from the regulatory authorities, or look it up on the Internet; it is important to reflect all the required parameters in it. It is best to entrust this work to specialists.




