Necessities fire truck classifications needed for better and coordinated organization of operational actions when extinguishing a fire by personnel of the Ministry of Emergency Situations. Before moving directly to the classification, it is necessary to understand what we started from, what characteristics and features were taken into account before classifying fire trucks.
Ensuring the fire safety of objects and territories is observed not only through preventive actions on the part of the authorities supervising and monitoring fire safety, but unfortunately there are cases when neglect of fire safety rules leads to dire consequences, which are often accompanied by a fire.
Fire extinguishing is already a direct task of the combat fire departments of the Ministry of Emergency Situations, which can only be carried out if there is good fire-fighting equipment and fire-fighting rescue equipment. The use of fire and rescue equipment is necessary due to the fact that uncontrolled combustion (fire) contributes to the appearance of significant temperatures near the fire and, as a consequence, the appearance of hazardous factors fire - smoke, soot, various toxic substances.
In this scenario, every minute is worth its weight in gold, so extinguishing the fire should be reduced to elementary destruction, due to the supply fire extinguishing agent to the source of the fire.
Since they may be subject to fire Various types substances with their own physical properties, physical state - fire extinguishing agents must be supplied under a certain pressure with a given intensity. The above qualities can be realized through the use fire equipment.
If we consider what fire fighting equipment is, we can say that it is a complex of technical means and devices various configurations and buildings used for extinguishing fires (or ensuring the conduct of fire extinguishing actions), localizing a fire, protecting people and material assets.
Today, firefighting equipment is represented by a variety of means, ranging from a basic fire extinguisher to a fire tank.
But if we consider the fire equipment necessary to extinguish fires, then we will consider in more detail fire truck classification.
Accordingly, with fire extinguishing tactics during a fire, there is often a need to carry out robotic work, rescue victims, open various structures using hand-held rescue tools (,) or. The above work can be carried out using special fire fighting equipment (vehicles) using special fire fighting tools.
Types of fire trucks
Thus, we will consider the following types of fire trucks depending on their purpose: main, special and auxiliary.
Each type of fire truck is designed to perform separate functions during fire fighting:
- basic fire trucks serve for transportation to the place emergency(fire) firefighters, water or other fire extinguishing agents to extinguish the fire and perform tasks as intended. In turn, this group is divided into cars:
- general purpose - for extinguishing fires in the residential and industrial sectors of cities and towns (fire pumps, first aid fire trucks);
- vehicles for intended use, adapted for extinguishing fires in production facilities in the production of which substances may be used, the extinguishing of which must be carried out with special fire extinguishing compounds, departmental facilities of the chemical, oil production and oil refining industries (air-foam extinguishing vehicles, gas-water, combined extinguishing, pumping station and etc.)
- special fire trucks serve to ensure special works in fire ( , articulated lifts, cars gas and smoke protection service, smoke removal, etc.)
- support vehicles these are the cars that belong to vehicles for servicing fire trucks, delivering personnel, fire, special and rescue equipment of the Ministry of Emergency Situations (fuel tankers, mobile repair shops, laboratories, buses, fuel trucks, etc.)
Symbols of fire trucks
To facilitate the identification of all types of fire trucks, it is customary to use an abbreviation indicating the functional affiliation of a fire truck to one type or another. This abbreviation is also commonly denoted on the sides of cars.
For example: fire tanker– AC, first aid fire truck – APP tanker truck, – ASA, etc.
Also, to make it easier to remember the characteristics of a fire truck, it is customary to add basic parameters to the basis of the special name of the vehicle: characteristics, productivity (such as 40 l/s in AC-40(130)63B) or lifting height of an articulated lift (30 m in AL-30(4310) )).
According to all fire trucks, it is customary to paint them red - which is commonly believed to symbolize fire, danger, etc. For greater sensitivity, the red color is diluted with wide white stripes.
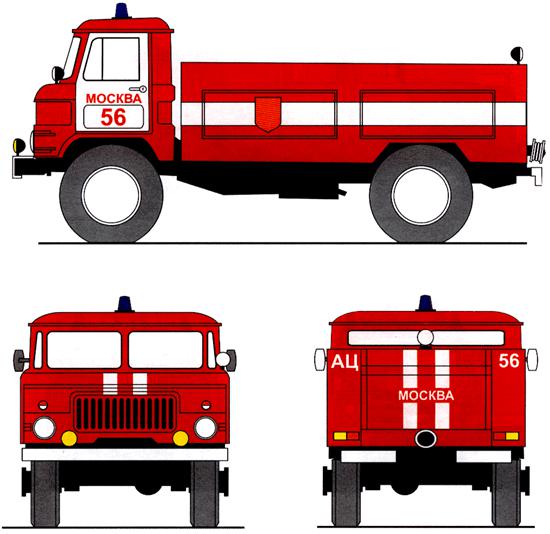
Also normative document the rules for placing inscriptions and identification marks are regulated.
So the number of the fire department to which the car belongs and the locality is indicated on the door of the car, and the type of fire truck (ANR) is indicated on the rear of the body.
To enhance the sensitivity of others and ensure that everyone understands that this is a fire truck, sound and signal beacons are also placed on it. Since a fire truck is a vehicle of increased care and importance, blue flashing lights are placed on it.
Concerning sound signal, then today the sound warning of others is made from an electric siren, although there was an option to reproduce a sound signal from the exhaust gases of the car through the gas exhaust system - (which explains the specific sound of fire trucks in old feature films).
Article No. 43 of Federal Law No. 123-FZ " Technical regulations on fire safety requirements"
Primary fire extinguishing means are intended for use by employees of organizations and personnel of departments fire department and other persons for the purpose of fighting fires and are divided into the following types:
- portable and mobile fire extinguishers;
- fire hydrants and means of ensuring their use;
- fire equipment;
- blankets to isolate the source of fire.
Classification of mobile fire extinguishing equipment
Article No. 44 of Federal Law No. 123-FZ "Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements"Mobile fire extinguishing equipment includes transportable or transportable fire trucks intended for use by personnel of fire departments when extinguishing fires. Mobile fire extinguishing equipment is divided into the following types:
- fire trucks (main and special);
- firefighting aircraft, helicopters;
- adapted technical means(tractors, trailers and tractors).
Classification of fire extinguishing installations
Article No. 45 of Federal Law No. 123-FZ "Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements"Fire extinguishing installations are a set of stationary technical means of extinguishing a fire by releasing a fire extinguishing agent. Fire extinguishing installations must ensure localization or elimination of fire.
Fire extinguishing installations by design are divided into:
- aggregate
- modular
- automatic
- automated
- manual
- water
- foam
- gas
- powder
- aerosol
- combined
- volumetric
- superficial
- locally volumetric
- local-superficial
Classification of fire automatic equipment
Article No. 46 of Federal Law No. 123-FZ "Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements"Facilities fire automatics intended for automatic detection fire, warning people about it and managing their evacuation, automatic fire extinguishing and switching on actuators of smoke protection systems, engineering and technological equipment buildings and objects.
Fire automatic equipment is divided into:
- fire detectors;
- Fire alarm control devices;
- fire control devices;
- technical means of warning and fire evacuation control;
- fire notification systems;
- other devices and equipment for constructing fire automatic systems.
Classification of personal protective equipment and fire rescue equipment
Article No. 47 of Federal Law No. 123-FZ "Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements"Facilities personal protection people in case of fire are designed to protect personnel of fire departments and people from the effects of dangerous fire factors. Means for rescuing people in case of fire are intended for self-rescue of personnel of fire departments and rescue of people from a burning building, structure, structure.
Personal protective equipment for people in case of fire is divided into:
- personal protective equipment for respiratory and visual organs;
- personal protective equipment for firefighters.
- individual means;
- collective means.
In accordance with fire safety rules in the Russian Federation PPB-01-93, fires are divided into 5 classes.
Class A – fires of solid substances, mainly of organic origin, the combustion of which is accompanied by smoldering (wood, textiles, paper, coal) and not accompanied by smoldering (plastic).
Class B – fires of flammable liquids or melting solids, insoluble in water (gasoline, ether, petroleum products), soluble in water (alcohol, methanol, glycerin).
Class C – gas fires.
Class D – fires of metals and their alloys.
Class E – fires associated with the burning of electrical installations.
Classification is necessary for the selection of fire extinguishing installations and primary fire extinguishing agents. The fire class of each fire extinguisher is indicated in the passport.
4 Classification of production facilities by fire hazard.
b, but not explode, liquids with a flash point of more than 61°C.
5 Fire prevention
Fire prevention is based on eliminating the conditions necessary for combustion and the principles of ensuring safety.
Security can be achieved:
1) Fire prevention measures
2) Alarm about fires.
5.1 Fire prevention measures
organizational ( correct operation machines and in-plant transport, proper maintenance of buildings and territories, fire safety training workers, organization of voluntary fire protection, issuance of orders on fire safety issues);
technical (compliance fire regulations, standards for design, installation of electrical wires and equipment, heating, ventilation, lighting, correct placement equipment);
security restrictions (prohibition of smoking in undesignated places, welding and other hot work in fire hazardous areas, etc.);
operational - timely preventive inspections, repairs and tests of process equipment.
In accordance with the rules PPB-01-93, to prevent fires, it is important to locate production in buildings of a certain fire resistance. Fire resistance is the resistance of buildings to fire.
Based on fire resistance, buildings are divided into 5 levels. The degree of fire resistance is characterized by the flammability of the substance and the fire resistance limit. The fire resistance limit of a building is the time, expressed in hours, after which the structure loses its load-bearing or enclosing capacity. Loss of load-bearing capacity means the collapse of a building structure in a fire. Loss of barrier ability means heating the structure to a temperature, an increase in which can cause spontaneous combustion of substances located in an adjacent room, or the formation of cracks in the structure through which combustion products can penetrate into adjacent rooms.
In accordance with the degree of fire resistance and the category of fire hazard of the production, the number of storeys of the building and fire breaks are determined.
Reducing the fire hazard of structures is of great importance.
Many rooms have wooden partitions, cabinets, shelving, etc. Increasing the flammability resistance of wooden structures is achieved by plastering them or lining them with fireproof or fire-resistant materials, deep or surface impregnation with fire-retardant compounds, and coating with fire-retardant paint or coating. Similar measures must be applied to other combustible structural materials.
The process of thermal decomposition of wood occurs in two phases:
the first phase of decomposition is observed when wood is heated to 250 (to the ignition temperature) and occurs with heat absorption;
the second phase - the combustion process itself occurs with the release of heat. The second phase consists of two periods of combustion of gas formed during the thermal decomposition of wood (flame phase of combustion) and combustion of the resulting charcoal (smoldering phase).
The flammability of wood is significantly reduced when it is impregnated with fire retardants. Heating wood leads to the decomposition of fire retardants with the formation of strong acids (phosphoric and sulfuric) and the release of non-flammable gases that prevent the burning and smoldering of the protected wood.
The most common fire retardants include ammonium phosphate, dibasic and monosubstituted, ammonium sulfate, borax and boric acid. Borax and boric acid are taken in a 1:1 mixture.
Thermal insulating materials include asbestos cement sheets, gypsum fiber, asbestos vermiculite, perlite boards, asbestos cardboard, and various plasters. Protection with these materials is used only in enclosed spaces.
Paints and coatings consist of a binder, filler and pigment. The resulting film in fire-retardant paints serves both fire-retardant and decorative purposes (due to the pigment).
Liquid glass, cement, gypsum, lime, clay are used as a binder for fire-retardant paints and coatings. synthetic resins etc. The fillers are chalk, talc, asbestos, vermiculite, etc. Pigments include methopane, zinc white, mummy, ocher, chromium oxide, etc.
The main methods of fire-retardant impregnation of wooden structures and products can be superficial and deep. In some cases fire retardant compounds are applied to the surface, in others they impregnate the material in baths or in deep impregnation units under pressure.
The effectiveness of a fire retardant is measured by the time after which a sample or structural element ignites from heat source. The cessation of combustion and smoldering after removal of the heat source determines the quality of the fire retardant composition.
The flammability characteristics of building materials and structures have been established:
ignition time;
burning rate;
time of cessation of combustion and smoldering after removal of the ignition source.
The burning rate is determined by the ratio of the percentage of weight loss of the sample under fire exposure to the test time. The study of flammability is carried out by testing standard samples of the material under specified heat sources, the position of these sources relative to the sample and the test time.
Fire extinguishing agents.
Fire extinguishing agents.
The impact of fire extinguishing agents on the source of a fire can be different: they cool the burning substance, isolate it from the air, and remove the concentration of oxygen and flammable substances. In other words, fire extinguishing agents act on the factors that cause the combustion process.
Principles of combustion termination.
Isolating the combustion source from air or reducing the oxygen concentration with non-flammable gases to a value at which combustion cannot occur:
cooling the combustion site below certain temperatures;
intensive speed braking chemical reaction in flames;
mechanical flame arrest by the action of a jet of gas or water;
creation of fire-barrier conditions.
To extinguish fires, water, aqueous solutions of chemical compounds, foam, inert gases and gas compositions, powders and various combinations of these agents are used.
Water is the main means of extinguishing fires. It is used for combustion of solid, liquid and gaseous substances and materials. The exception is some alkali metals and other compounds that decompose water. Water for extinguishing is used in the form of solid (compact) jets, in a sprayed and finely sprayed (fog-like) state, and also in the form of steam.
The ability to extinguish a fire with water is based on its cooling effect, dilution of the flammable medium, water vapor formed during evaporation and mechanical effect on the burning substance (flame failure).
Foams are an effective and convenient fire extinguishing agent and are widely used to eliminate the combustion of various substances, especially flammable and combustible liquids.
Foam is a cellular-film system consisting of a mass of gas or air bubbles (cells) separated by thin films of liquid.
Fire extinguishing foams are divided into two groups according to the method of formation: chemical and air-mechanical.
Chemical foam is produced in large quantities in foam generators by contacting foam powders with water, consisting of an alkaline part (bicarbonate of soda), an acid part (aluminum sulfate) and a foaming agent (substances of protein origin, synthetic, various surfactants, etc.).
In chemical foam fire extinguishers foam is formed by the reaction of aqueous solutions of sodium bicarbonate containing licorice extract, sulfuric acid and iron tanning agent.
Chemical foam is approximately 80% carbon dioxide, 19.7% water and 3% foaming agent.
Air-mechanical foam is formed in generators as a result of mechanical mixing of air, water and foaming agent and comes in low, medium and high expansion. Depending on the type of foam concentrate and the foam expansion ratio, it is used to extinguish flammable liquids and combustible liquids.
Air-mechanical foam is economical, non-electrically conductive, harmless to people, can be easily and quickly produced during a fire, and, unlike chemical foam, does not cause metal corrosion and does not damage equipment and materials on which it comes in contact.
The main fire extinguishing property of foam is its ability to isolate the burning substance and materials from the surrounding air, reduce the concentration of oxygen in the combustion zone, as well as its cooling effect.
Gas fire extinguishing agents. These means include: water vapor, carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide), inert gases (nitrogen, argon), as well as fire extinguishing compounds based on halogenated hydrocarbons, which are gases or highly volatile liquids (ethyl bromide, chlorobromomethane).
Carbon dioxide in snow-like and gaseous states is used in various fire extinguishers and stationary installations to extinguish fires in enclosed spaces and small open fires.
Inert gases are used to fill volumes in which, when the oxygen concentration is reduced to 5% or lower, hot work can be performed (cutting, welding metals, etc.).
Powdered substances are dry compositions based on sodium carbonate and bicarbonate. Powders are used to extinguish metals and various solid and liquid flammable substances and materials.
Powder compositions are non-toxic, do not have a harmful effect on materials and can be used in combination with sprayed water and foam extinguishing agents. A negative property of powders is that they do not cool burning substances, and they can re-ignite from heated structures.
STATIONARY FIRE FIGHTING INSTALLATIONS AND DEVICES.
Stationary fire extinguishing installations consist of permanently installed apparatus and devices connected by a pipeline system for supplying fire extinguishing agents to the protected objects.
Automatic fire extinguishing installations are classified depending on the use of extinguishing agents:
water - using solid, atomized, finely atomized water jets;
water chemical - using water with various additives (wetting agents, thickeners, etc.);
foam - using air-mechanical foam;
gas - using carbon dioxide, halogenated hydrocarbons, inert gases;
powder - using fire extinguishing powders;
combined - using several extinguishing agents.
One of the promising areas that ensures fire safety of objects is the installation of fire-fighting automatics - sprinkler and deluge systems (terms taken from English words: to sprinkle - splash and to drench - wet). These installations are used by many commercial warehouses.
Sprinkler systems are designed for quick automatic extinguishing and localization of a fire when water can be used as a fire extinguishing agent. Simultaneously with the supply of sprayed water to the fire, the system automatically gives a fire signal.
In sprinkler installations, air-mechanical foam can also be used as a fire extinguishing agent.
Sprinkler installations, adapted for extinguishing with air-mechanical foam, are equipped instead of SP-2 sprinkler heads with special foam heads (OP foam sprinkler), allowing one head to protect a floor area of 20 - 25 m2. To form air-mechanical foam in installations, a 3–5% solution of foaming agent PO-1 is used.
Depending on the temperature in the protected premises, sprinkler systems are divided into water, air and air-water.
Water sprinkler systems are installed in rooms where the temperature is constantly maintained above 4°C. The pipelines of this system are always filled with water. When the air temperature rises or is exposed to flame, the fusible locks of the sprinkler heads are unsoldered, water comes out of the holes, irrigating the protection zone.
Air sprinkler systems are installed in unheated buildings. The pipelines of this system are filled with compressed air. In this case, there is compressed air before the control and alarm valve, and water after the control and alarm valve. When the sprinkler head of the air system is opened, after the air has escaped, water enters the network and extinguishes the fire.
Air-water systems are a combination of air and water sprinkler systems. The sprinkler installation is activated automatically by melting the fusible lock of the sprinkler head.
Deluge installations are designed for automatic and remote fire extinguishing with water. There are automatic and manual deluge installations. In automatic deluge installations, water is supplied to the network using a group-action valve. Under normal conditions, the automatic inducement valve is held in the closed position by a cable system with fusible locks. In the event of a fire, the lock melts, the cable breaks, the valve opens under water pressure and water flows into the deluge. In a manual deluge plant, water is supplied after the valve is opened. Unlike splicler systems, in deluge installations, water sprayers (deluges) are constantly open.
Fire extinguishers are designed to extinguish fires in their initial stages. Based on the type of fire extinguishing agent used, they are divided into foam, gas and powder.
Foam fire extinguishers are designed to extinguish small fires of solid materials and substances and flammable liquids. They are not used to extinguish fires in electrical installations that are under voltage, because chemical foam is electrically conductive.
Chemical foam fire extinguishers OHP-10, OP-M.
Air-foam fire extinguishers OVP-5, OVP-10.
Carbon dioxide fire extinguishers OU-2, OU-5, OU-8 are used to extinguish various substances and materials (with the exception of alkali metals), live electrical installations, vehicles, etc.
Carbon dioxide-bromoethyl fire extinguishers OUB-3A and OUB-7A are designed to extinguish small fires of various flammable substances, smoldering materials, and live electrical installations.
Powder fire extinguishers OP-1, OP2B, OP-10 are designed to extinguish small fires of flammable liquids, gases, live electrical installations, metals and their alloys.
Automatic aerosol fire extinguisher SOT-1 - designed to extinguish fires of solid and liquid flammable substances (alcohols, gasoline), smoldering and solid materials, electrical equipment in closed spaces.
The operating principle is based on the strong inhibitory effect of a fire extinguishing aerosol composition made from ultrafine products on the combustion reactions of substances in air oxygen.
The aerosol has no harmful effects on humans and is easily removed. Disposable fire extinguisher.
The UAP-A fire extinguisher automatically detects and extinguishes fire in small confined spaces. The fire extinguisher is installed on the ceiling in the center of the room. If a fire occurs, the fusible element is destroyed, the fire extinguisher container is opened and a substance (freon or powder) is released into the room, creating an environment that does not support combustion.
FIRE ALARM.
To fight fires important has a timely report of a fire. To report a fire, use electrical and automatic system alarms.
Successfully fighting a fire depends on quickly and accurately reporting the fire and its location to the local fire brigade. For this purpose, electric (EPS), automatic (APS), and sound fire alarm systems can be used, which include a horn, siren, etc. Telephone and radio communications are used as a means of fire alarm.
The main elements of electrical and automatic fire alarms are detectors installed at objects, receiving stations that register the outbreak of a fire, and linear structures connecting detectors to receiving stations. Reception stations located in special fire department premises must be manned 24 hours a day.
Basic requirements for fire alarms:
must be located in places accessible for inspection;
sensors must be highly sensitive.
Sensors are used thermal, smoke, ultrasonic and combined.
Sensors can be: maximum – they are triggered when the controlled parameters reach a given value; differential – react to changes in the speed of a given parameter; maximally differential – they react to both.
The principle of operation of thermal sensors is to change the physical and mechanical properties of sensitive elements under the influence of temperature (low-melting alloy). An alloy is used to connect two plates. When heated, the alloy melts, the plates open the electrical circuit, and a signal is sent to the remote control.
Smoke detectors have two main methods of detecting smoke: photoelectric (PDE) and radioisotope (RID). The IDF detector detects smoke by detecting light reflected from smoke particles with a photocell. The RID has an ionization chamber with a source of α-particles as a sensitive element. An increase in smoke content reduces the rate of ionization in the chamber, which is recorded.
A combined detector (CD) responds to both rising temperatures and smoke.
A light fire detector (SI) detects the radiation of a flame against the background of extraneous light sources.
The ultrasonic sensor has high sensitivity and can combine security and alarm functions. These sensors respond to changes in the characteristics of the ultrasonic field filling the protected room.
Currently, enterprises use beam and ring electric fire alarms.
Beam fire alarm system TOL-10/50 is used in enterprises with round-the-clock presence of people and provides reception of signals, phone conversation with a detector, launch of stationary fire extinguishing installations.
The ring fire alarm system TKOZ-50M is designed for 50 manual detectors. The station provides signal reception, recording by a recording device and automatic transmission of the signal to the fire department.
In premises where people are not present 24/7, automatic fire detectors are installed. The triggering factor for these detectors is smoke, heat, light, or both factors combined.
Reliable fire communications and alarms play an important role in the timely detection of fires and calling fire departments to the scene of a fire. By purpose, fire communications are divided into:
notification communication;
dispatch communication;
The word “fire” evokes horror in every person. Fire is a completely uncontrollable phenomenon that destroys everything in its path. Therefore, people need to know as much as possible about it in order not only to resist it, but also to be able to prevent it. So, let's see what the classification of fires is.
There are several types of classifications:
1. Fires are divided by rank. It should be said that such a division is simply necessary. This is necessary in order to correctly calculate the required number of equipment and people at a crucial moment. There are basically six types of fires:
If a signal about smoke is received, two cars go to the place of the call. If a fire is confirmed, firefighters immediately begin extinguishing it. This is type 1.
If the fire intensifies, two additional vehicles are called to the scene of the tragedy. And now 4 departments are already working at the scene. This type is 1BIS
Two additional vehicles are dispatched if the area of the fire increases and there is no source of water nearby. So, if there are 6 branches on a call, this is rank No. 2.
If the situation escalates even more, and 10 squads are involved in extinguishing the fire, this is already rank No. 3.
When calling type 4, 13 departments work at the scene of a fire.
If the situation is heated to the limit, and 15 branches are working on a call, this is rank No. 5.
2. There is also a classification of fires according to the type of fire location:
If the fire occurred in production areas, warehouses or a factory, it is an industrial type.
If a fire happened in a domestic apartment.
And, of course, if forests, steppes and swamps are burning, this is a natural type.
3. There is a classification of fires based on the density of buildings at the site of the fire:
If a separate building is on fire, and the building density does not exceed the safe one (20%) - this is the so-called separate type of fire.
If the fire covers an area that is 20% or 30% built up, this is a continuous type.
If the building density is more than 30%, the fire has a colorful name - “a terrible fire storm.”
And the last type is smoldering.
4. Another classification of fires, depending on what substances are burning:
Class "A" - solids:
Coal is burning or smoldering, textiles - A1;
Plastic burns, but does not smolder - A2.
Class “B” - liquid substances:
Gasoline, ether and petroleum products burn, that is, those substances that do not dissolve in water - B1;
Alcohol or glycerin burns, that is, substances soluble in water.
Class “C” - gas fire, for example, propane.
Class “D” - metals burn:
Light metals - D1;
Alkaline - D2;
Compounds that contain metal - D3.
Class “E” - electrical installations were damaged by fire.
Class “F” - radioactive waste burns.
5. Another classification reflects the types of fires depending on the depth of the fire:
Fire in transport.
Fire of fields or steppes.
Fire at depth, in a mine or pit.
Buildings are burning.
The causes of fires are varied. The main one is - Also, the most common reasons include non-compliance with fire safety, spontaneous combustion of substances, lightning, arson, improper use household appliances etc.
Fire fighting consists of two parts: prevention and immediate action during a fire. Basic methods of prevention: periodic checking of electrical wiring (sockets, adapters, etc.), timely replacement of old household appliances, caution in handling electricity, etc. In order to defeat a fire, it is necessary to first eliminate the source of the fire itself, and then extinguish the rest flame. The most available funds fire extinguishers should always be nearby. These include sand and a fire extinguisher. Water, various tarpaulins or clothing are also used.
Remember, very often fire takes the lives of innocent people, be careful with fire!
Article 41. Purpose of classification
The classification of fire equipment is used to determine its purpose, scope of application, as well as to establish fire safety requirements for the operation of fire equipment.
Article 42. Classification of fire equipment
Firefighting equipment, depending on its purpose and area of application, is divided into the following types:
1) primary fire extinguishing means;
2) mobile fire extinguishing equipment;
3) fire extinguishing installations;
4) fire automatic equipment;
5) fire fighting equipment;
6) means of personal protection and rescue of people in case of fire;
7) firefighting tools (mechanized and non-mechanized);
8) fire alarms, communications and notification.
Article 43. Classification and scope of primary fire extinguishing agents
Primary fire extinguishing means are intended for use by employees of organizations, personnel of fire departments and other persons to fight fires and are divided into the following types:
1) portable and mobile fire extinguishers;
2) fire hydrants and means of ensuring their use;
3) fire equipment;
4) blankets to isolate the source of fire.
Article 44. Classification of mobile fire extinguishing equipment
1. Mobile fire extinguishing equipment includes transportable or transportable fire trucks intended for use by personnel of fire departments when extinguishing fires.
2. Mobile fire extinguishing equipment is divided into the following types:
1) fire trucks (main and special);
2) firefighting aircraft, helicopters;
3) fire trains;
4) fire ships;
5) fire motor pumps;
6) adapted technical means (tractors, trailers and tractors).
Article 45. Classification of fire extinguishing installations
1. Fire extinguishing installations - a set of stationary technical means of extinguishing a fire by releasing a fire extinguishing agent. Fire extinguishing installations must ensure localization or elimination of fire. Fire extinguishing installations according to their design are divided into modular and modular, according to the degree of automation - into automatic, automated and manual, according to the type of fire extinguishing agent - into water, foam, gas, powder, aerosol and combined, according to the method of extinguishing - into volumetric, surface, local - volumetric and local-surface.
2. The type of fire extinguishing installation, extinguishing method and type of fire extinguishing agent are determined by the design organization. In this case, the fire extinguishing installation must provide:
1) implementation effective technologies fire extinguishing, optimal inertia, minimal harmful effects on the protected equipment;
2) activation within a time period not exceeding the duration of the initial stage of fire development (critical time of free development of the fire);
3) the required intensity of irrigation or specific consumption of fire extinguishing agent;
4) extinguishing a fire in order to eliminate or localize it within the time necessary for the deployment of operational forces and means;
5) required reliability of operation.
Article 46. Classification of fire automatic equipment
Fire automatic equipment is designed to automatically detect a fire, notify people about it and control their evacuation, automatic fire extinguishing and activation of actuators of smoke protection systems, control of engineering and technological equipment of buildings and facilities. Fire automatic equipment is divided into:
1) fire detectors;
2) fire alarm control devices;
3) fire control devices;
4) technical means of warning and fire evacuation control;
5) systems for transmitting fire notifications;
6) other instruments and equipment for constructing fire automatic systems.
Article 47. Classification of personal protective equipment and rescue of people in case of fire
1. Personal protective equipment for people in case of fire is intended to protect personnel of fire departments and people from exposure to dangerous fire factors. Means for rescuing people in case of fire are intended for self-rescue of personnel of fire departments and rescue of people from a burning building, structure, structure.
2. Personal protective equipment for people in case of fire is divided into:
1) personal protective equipment for respiratory and visual organs;
2) personal protective equipment for firefighters.
3. Means of rescuing people from heights in case of fire are divided into:
1) individual means;
2) collective means.




